Figure 5.
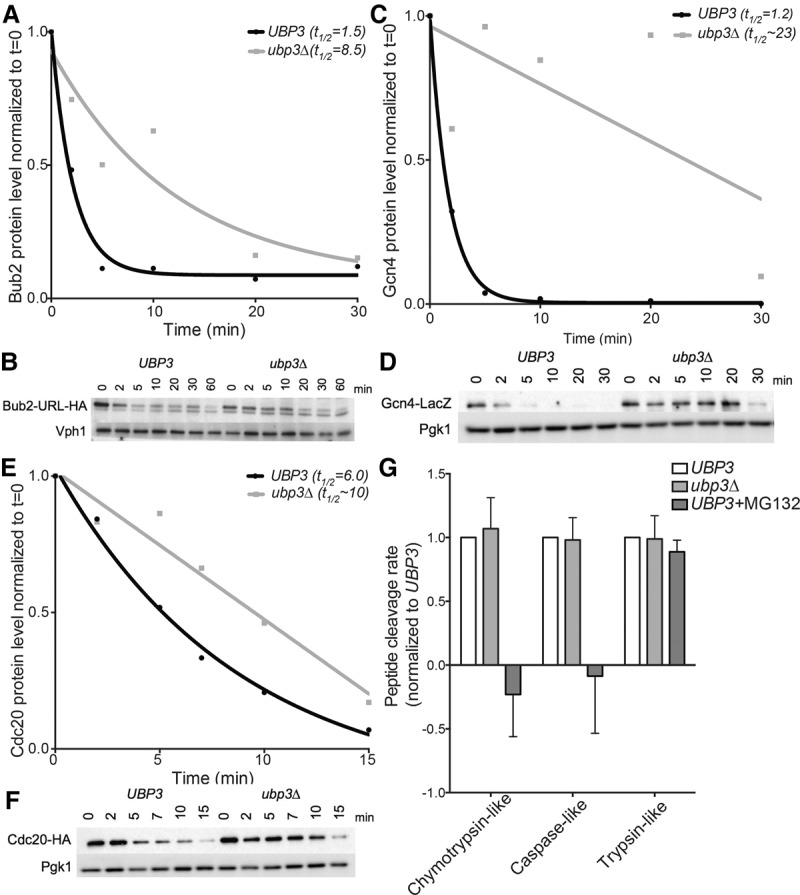
Deletion of UBP3 increases the half-lives of known ubiquitin–proteasome substrates without affecting the in vitro catalytic activity of the proteasome. (A–F) Cells were grown overnight in medium containing raffinose at room temperature, and expression of tagged substrates was induced by the addition of 2% galactose for 45 min. The t = 0 sample was taken before the addition of 2% glucose and 50 µg/mL cycloheximide. Samples were taken at the indicated times after cycloheximide addition, and protein levels were analyzed by Western blot analysis. Quantifications relative to the loading control and normalized to time = 0 are plotted in A, C, and E. (A,B) The half-life of Bub2 in wild-type cells and cells lacking UBP3. Vph1 was used as a loading control. (C,D) The half-life of Gcn4 in wild-type cells and cells lacking UBP3. Pgk1 was used as a loading control. (E,F) The half-life of Cdc20 in wild-type cells and cells lacking UBP3. Pgk1 was used as a loading control. (G) The in vitro proteasome activity of UBP3 and ubp3Δ cell lysates was determined using cleavage of fluorogenic substrates as a readout for protease activity. MG132 was added to wild-type lysates to inhibit the activity of two of the three peptidase activities of the proteasome.
