Figure 2.
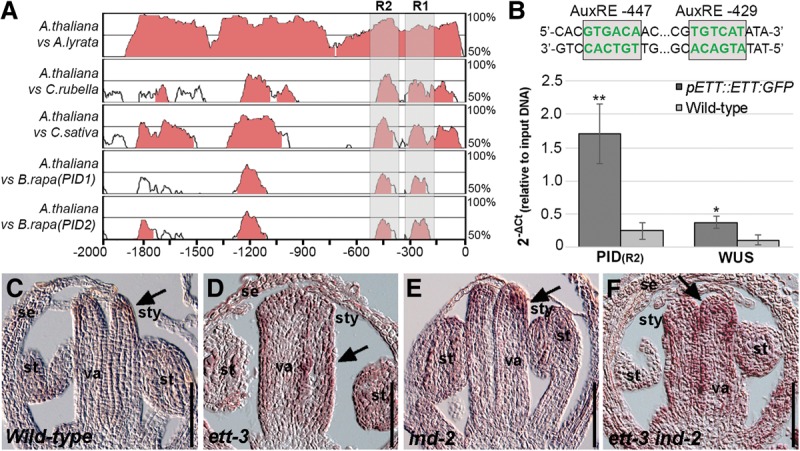
ETT and IND function together to regulate target genes during gynoecium development. (A) Phylogenetic shadowing using mVISTA of a 2-kb genomic region upstream of the translational start site of the PID gene with pairwise alignments of Arabidopsis thaliana with Arabidopsis lyrata, Capsella rubella, Camelina sativa, and Brassica rapa. Regions 1 and 2 (R1 and R2) are indicated by shaded areas. (B) ChIP with the pETT::ETT-GFP line showing enrichment of a fragment containing the conserved AuxRE sites at −429 and −447. The WUS promoter was used as a positive control. Error bars show standard deviation. (*) P < 0.01; (**) P < 0.001. (C–F) In situ hybridization of PID mRNA at the apex of stage 8 gynoecia from Col-0 (C), ett-3 (D), ind-2 (E), and ett-3 ind-2 (F). (se) Sepal; (st) stamen; (stg) stigma; (sty) style; (va) valve. Bars, 50 μm.
