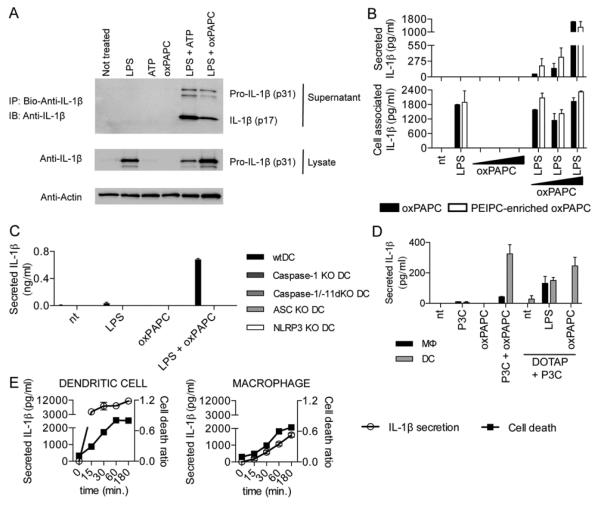
Fig. 2. oxPAPC induces the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in DCs.
(A) DCs primed with LPS, followed by ATP or oxPAPC treatment. Cell culture supernatant from DCs subjected to indicated treatments were collected, and processed IL-1β (p17) production was assessed. One experiment representative of three is shown. (B) DCs were treated with LPS alone, 10, 50, or 120μM oxPAPC or were primed with LPS for 3 hours and then treated with oxPAPC. For this experiment, commercially available oxPAPC and an oxPAPC enriched in PEIPC were used. 18 hours after LPS administration, secreted (left panel) and cell associated (right panel) IL-1β were measured by ELISA. Means and standard deviations of four replicates are shown. (C) DCs of the genotypes indicated were treated with LPS alone, oxPAPC alone or were primed with LPS for 3 hours and then treated with oxPAPC. 18 hours after LPS administration, IL-1β and secretion was measured by ELISA. Means and standard deviations of four replicates are shown. (D) MΦs and DCs were treated with Pam3CSK (P3C) alone, oxPAPC alone, or were primed with Pam3CSK for 3 hours and then treated with oxPAPC, DOTAP alone, and LPS or oxPAPC encapsulated in DOTAP. 18 hours after P3C administration, IL-1β was measured by ELISA. Means and standard deviations of four replicates are shown. (E) DCs (left panel) or MΦs (right panel) were primed with LPS for three hours and treated with ATP. At indicated time points, IL-1β was measured by ELISA and cell death was measured by PI permeabilization assay. Means and standard deviations of four replicates are shown.