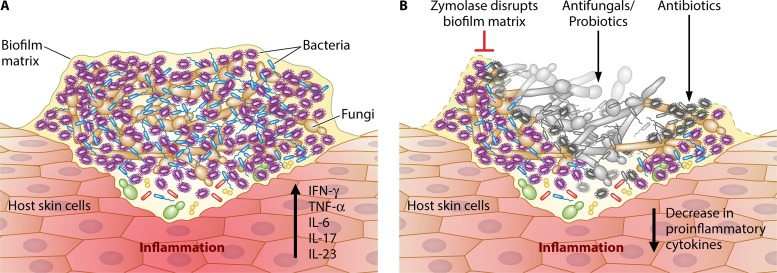
FIG 1 .
Interkingdom cooperation between fungi and bacteria. Chronic wounds are complex systems of multispecies fungal and bacterial biofilms. These biofilms provide a protected milieu for microbes living in close proximity. Fungal cells form the biofilm core while bacteria associate around the periphery of the cells. The fungal hyphae and microbial-secreted enzymes/metabolites facilitate invasion of the skin epidermis/dermis leading to host tissue damage and inflammatory response manifested by an increase in proinflammatory cytokine production (panel A). Panel B shows disruption of the biofilm matrix by zymolase thereby unmasking the microbes. Consequently, treatment with antifungal agents (e.g., echinocandins) and antibiotics leads to microbial cell death (gray/black color) and a decrease in the production of proinflammatory cytokines. IFN-γ, gamma interferon; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-6, -17, and -23, interleukins 6, 17, and 23, respectively.