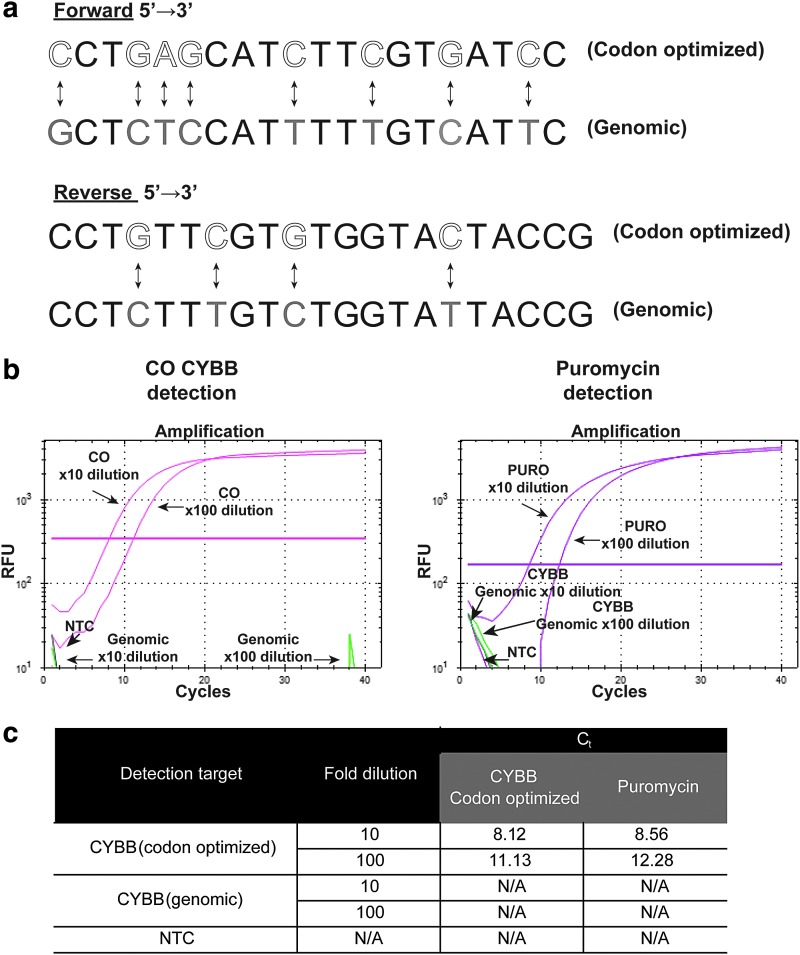
Figure 1.
Primer design and target specificity. (a) Bidirectional arrows indicate differences in primer design targeting either codon-optimized (CO) (white letters) or genomic (gray letters) CYBB sequences. (b) Amplification curves for the detection of CO CYBB and the puromycin resistance gene (PURO) (pink). As a control, primer probes targeting genomic CYBB (green) were included within the same reaction samples. The plasmid pAlpha.SIN.EFS.gp91s.F2A.PURO.T2A.ΔLNGFR.oPRE was diluted to 10 and 100 times. The horizontal pink line represents Ct (threshold cycle) values. NTC, no-template control; RFU, relative fluorescence units. (c) Tabular summary of CO CYBB and PURO detection alongside respective Ct values. N/A, not applicable (indicates no detection); NTC, no-template control.