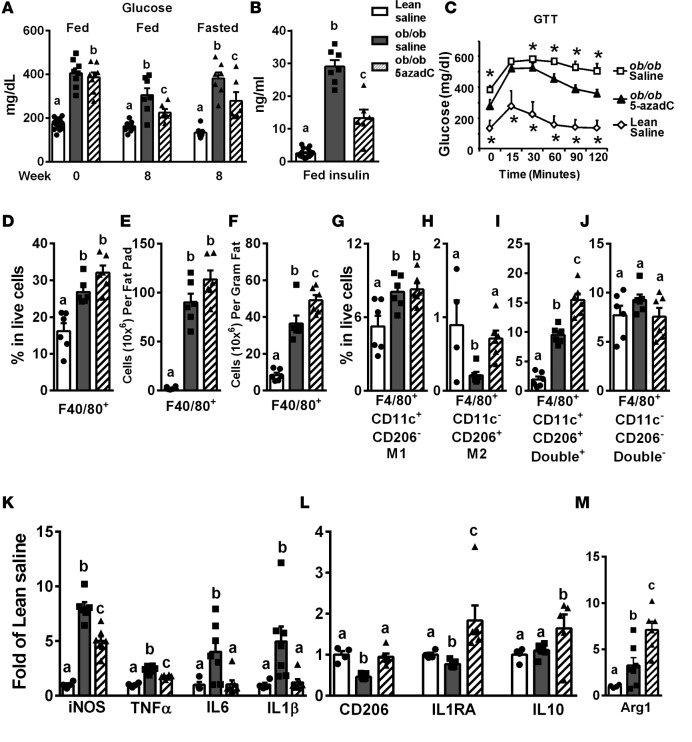
Figure 5. Inhibiting DNA methylation by 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine improves insulin sensitivity, promotes adipose tissue macrophage (ATM) alternative polarization and suppresses ATM inflammation in ob/ob mice.
(A) Blood glucose levels in ob/ob and lean mice before and 8 weeks after 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-azadC) treatment (0.25 mg/kg 3 times per week). (B) Serum insulin levels in ob/ob and lean mice after 8 weeks of 5-azadC treatment. (C) Glucose tolerance test (GTT) in ob/ob and lean mice after 8 weeks of 5-azadC treatment. (D and F) Percentage of F4/80+ ATMs in live stromal vascular fraction (SVF) cells (D), F4/80+ ATM content per epididymal fat pad (E), and F4/80+ ATM content per gram of fat (F) in ob/ob and lean mice treated with saline or 5-azadC for 8 weeks. (G–J) Percentage of F4/80+CD1c+CD206– M1 ATMs (G), F4/80+CD1c–CD206+ M2 ATMs (H), F4/80+CD1c+CD206+ double+ ATMs (I), and F4/80+CD1c–CD206– double– ATMs in live SVF cells isolated from ob/ob and lean mice treated with saline or 5-azadC for 8 weeks. (K–M) M1 and M2 marker expression in ATMs isolated from adipose tissue of ob/ob and lean mice treated with saline or 5-azadC for 8 weeks. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. n = 6–16. *P < 0.05 vs. other groups. Groups labeled with different letters are statistically different from each other. Differences between groups were analyzed for statistical significance by Student’s t test, ANOVA with Fischer’s probable least-squares difference post hoc test, or ANOVA with repeated measures.