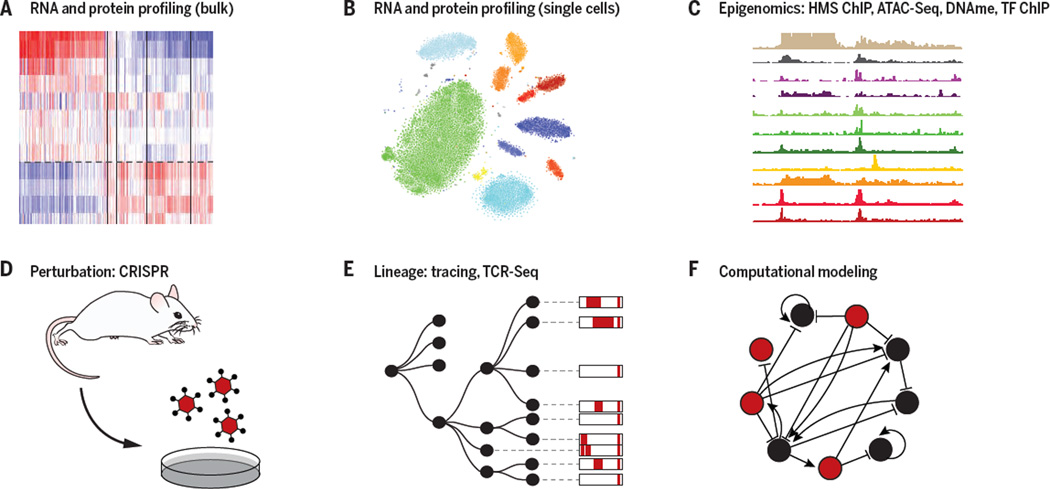
Figure 2. Genomic tools for dissecting immune-environment interactions.
Shown are key components of the current genomic tool box, including profiling of RNA, protein and protein modification levels in bulk samples (A) and single cells (B), epigenomic measurements of TF binding, histone modification, DNA methylation, and chromatin accessibility (C), the ability to systematically perturb genes through genome engineering (D) or natural variation, tracing of cells with engineered molecular barcodes or TcR and BcR clonality (E), and computational algorithms that use profiling and perturbation data to infer genetic causality and molecular mechanisms (F).