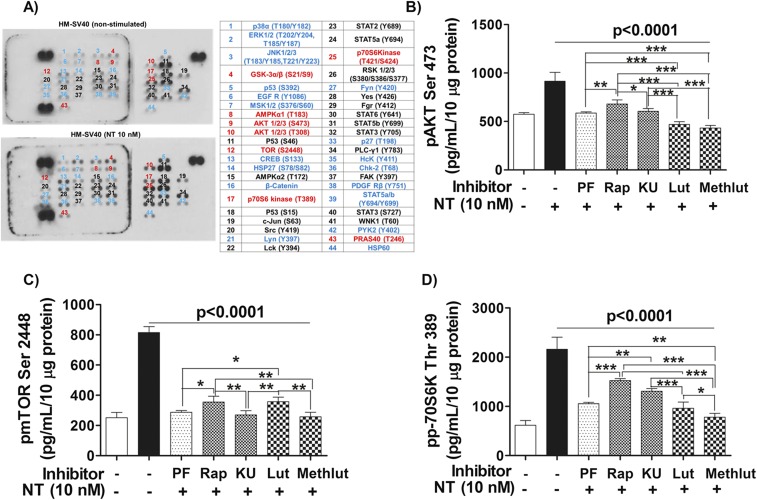
Fig. S4.
NT stimulation of HM-SV40 involves activation of mTOR signaling, which is inhibited by luteolin (Lut) and methoxyluteolin (Methlut). (A) Immortalized HM-SV40 (10 × 106 cells) were serum-starved overnight and then stimulated with NT (10 nM) for 30 min before cellular lysates were harvested to probe for the phosphorylated levels of intracellular signaling kinases, as shown using a human phosphoarray blot. Increased levels of several phosphoproteins (blue), including components of the mTOR signaling pathway (red), were denoted in NT-stimulated microglia after qualitative comparisons with control cells were made. All conditions were performed in the single blot shown (n = 1). HM-SV40 (1 × 106 cells) were serum-starved and pretreated with PI3K/mTOR inhibitors (0.5 μM) and the flavonoids (Lut and Methlut, 5 μM) overnight, and then stimulated with NT (10 nM) for 30 min to measure the protein levels of the mTORC2 substrate pAKTSer473 (B), pmTORSer2448 (C), and the downstream mTORC1 substrate pp70S6KThr389 (D) using specific phospho-ELISA kits. All conditions were performed in triplicate for each dataset and were repeated three times (n = 3). Significance of comparisons was determined for stimulated cells and for those cells with inhibitors/flavonoids, as denoted by the horizontal lines (P < 0.0001), and also among all of the inhibitor/flavonoid treatments shown by the horizontal brackets and by corresponding *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, and ***P < 0.0001. Rap, rapamycin.