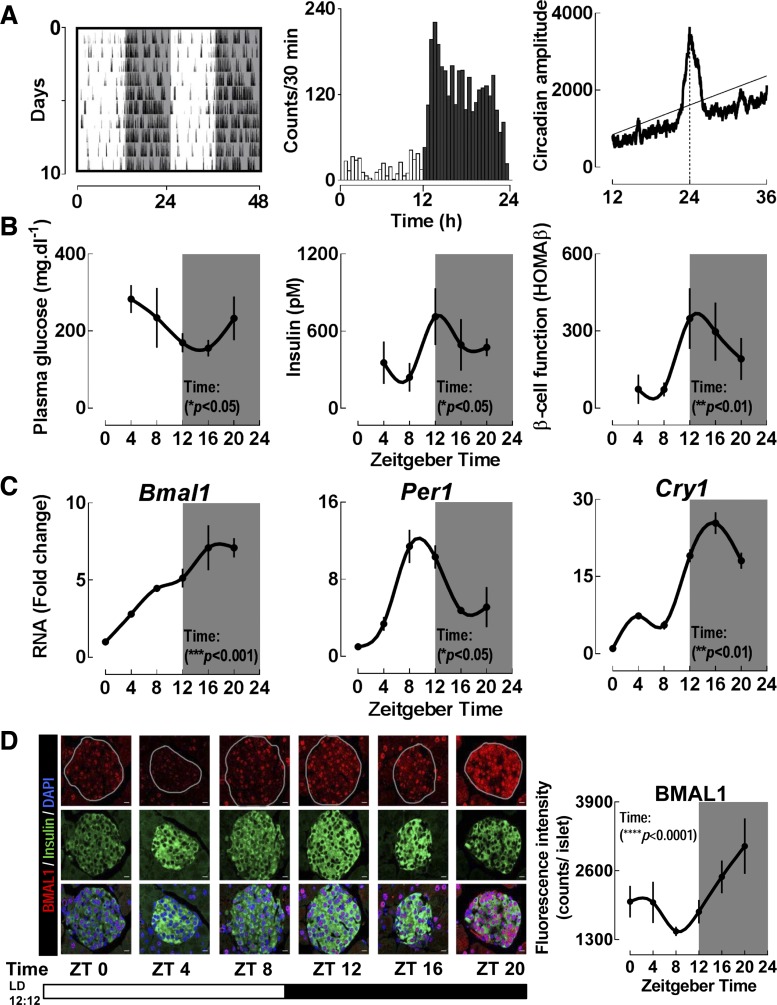
Fig. 1.
C57BL6 mice display significant diurnal variations in behavioral, physiological, and molecular parameters. A: representative activity recordings in a C57BL6 mouse (n = 9 examined) monitored for 10 days under light-dark (LD) cycle. Shaded areas represent periods of dark (left). Mean circadian activity (expressed as activity counts/30 min) across the 24 h circadian day (center). χ2 periodogram analysis demonstrating the dominant circadian period of exactly 24 h in a representative mouse under LD cycle (right). Solid horizontal line represents statistically significant threshold in determination of the dominant circadian period. Broken vertical black line represents dominant circadian period of exactly 24 h. B: assessment of diurnal plasma glucose, insulin, and homeostatic model assessment of beta cell function (HOMA-β). Each time point represents mean ± SE (n = 6–7 per group). Statistical significance was determined by repeated-measures 1-way ANOVA and shows significant effects of “Time” (P < 0.05) for each metabolic parameter. C: assessment of diurnal mRNA expression of selected key clock genes (Bmal1, Per1, and Cry1) from islet lysates isolated across the 24 h circadian day (n = 3–4 per time point). Statistical significance was determined by repeated-measures 1-way ANOVA and shows significant effects of “Time” (P < 0.05) for every clock gene. Quantitative PCR analysis was used to determine ΔΔCT based fold-changes in expression of clock genes utilizing GAPDH as the endogenous control gene. D: representative examples and corresponding quantification of pancreatic islets stained by immunofluorescence for BMAL1 in red and insulin in green imaged at ×63 magnification from C57BL6 mice collected at 4 h intervals (n = 3 at each time point) across the 24 h day (scale bars, 25 μm). Statistical significance was determined by repeated-measures 1-way ANOVA and shows significant effects of “Time” (P < 0.05). ZT, Zeitgeber time.