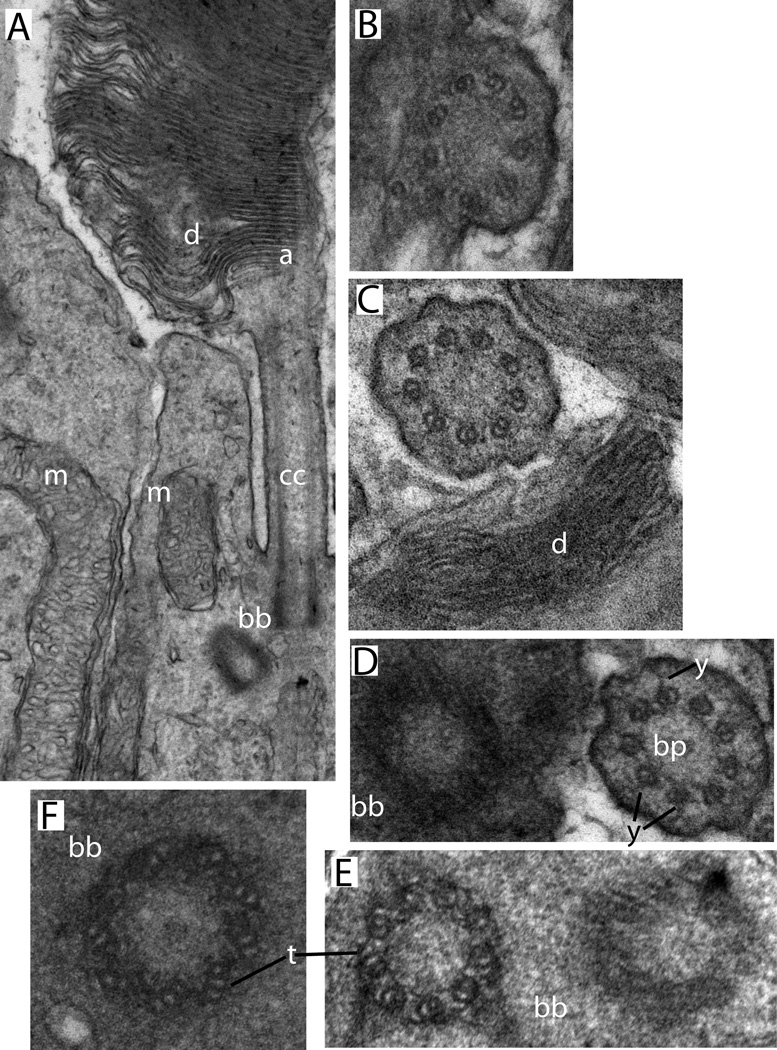
Figure 2.
Conventional transmission electron microscopy of mouse rod sensory cilium. Sample preparation and imaging were as described in (He et al., 2016). A. Longitudinal section showing connecting cilium and adjacent regions of outer and inner segments (Labels: d, disks; cc, connecting cilium; bb, basal body complex; a, axoneme; m, mitochondria). B-F, cross-sectional views through the same regions. B, a region where the CC membrane is continuous with the plasma membrane. C, a connecting cilium sectioned near the base of the outer segment (d, disks). D, a centriole next to a connecting cilium from an adjacent cell (y, y-links; bp, base plate or terminal plate, a structure observed within the lumen of the transition zone immediately above the mother centriole). E, a basal body complex (bb), showing the triplet microtubules (t) of one centriole. F. An isolated centriole with visible microtubule triplets (t).