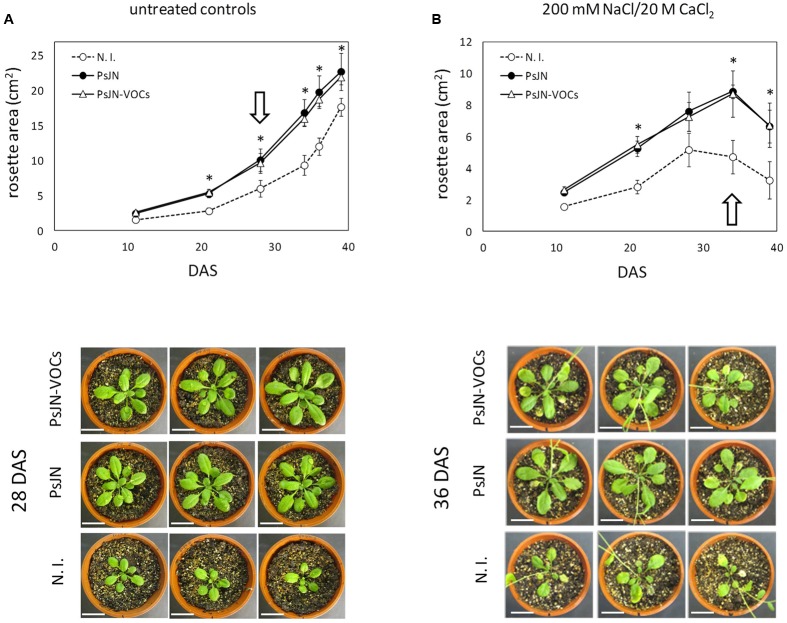
FIGURE 3.
Long-term effects of exposure to volatile emission from P. phytofirmans. Arabidopsis seeds were exposed to PsJN volatiles (PsJN-VOCs), directly inoculated with the bacterium (PsJN), or non-inoculated (N. I.) in the dual plate system for 11 DAS, and plantlets were transferred to soil. Transferred plants were irrigated three times a week. Untreated controls received only standard irrigation water (A), while treated plants received 2 irrigations with standard water and a third containing 200 mM of NaCl and 20 mM of CaCl2 (B). Images of 10 representative plants taken at different times, and rosette area was measured for each treatment. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences among PsJN and N. I: plants within each measured time point, which were explored using One-Way ANOVA Tukey’s HSD tests; p < 0.05. Images of representative plants are shown below each treatment, representing time points (DAS) with the highest differences in rosette area for untreated controls and salt irrigated plants (highlighted by white arrows).