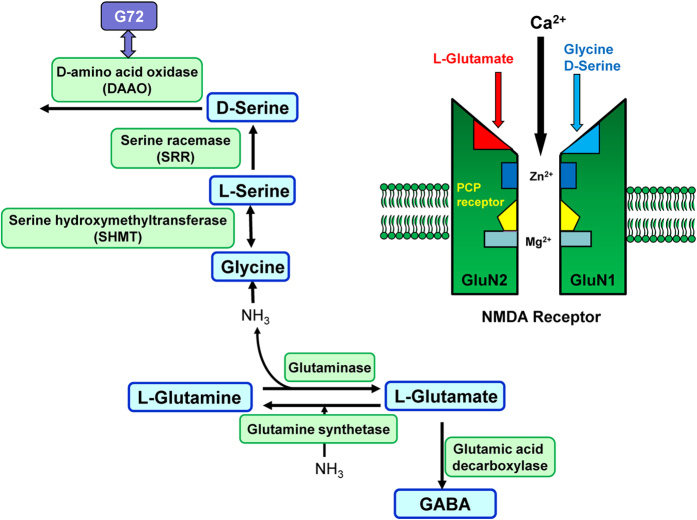
Figure 5. Synthetic and metabolic pathway of amino acids and NMDA receptor.
L-Glutamate, an excitatory amino acid, is synthesized from L-glutamine by glutaminase, and metabolized to L-glutamine by glutamine synthetase. In addition, L-glutamate is metabolized to γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), an inhibitory amino acid, by glutamic acid decarboxylase. D-Serine is synthesized from L-serine by serine racemase (SRR), and is metabolized by D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO). L-Serine is converted to glycine by serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT). Phencyclidine (PCP) is an ion-channel blocker of the NMDA receptor. Glycine and D-serine are endogenous co-agonists of the glycine modulatory site on the GluN1 subunit. Glutamate is an endogenous agonist at glutamate sites on the GluN2 subunit. Thus, glutamine-glutamate-GABA cycle plays a key role in the NMDA receptor neurotransmission. (A slight modification with ref. 8).