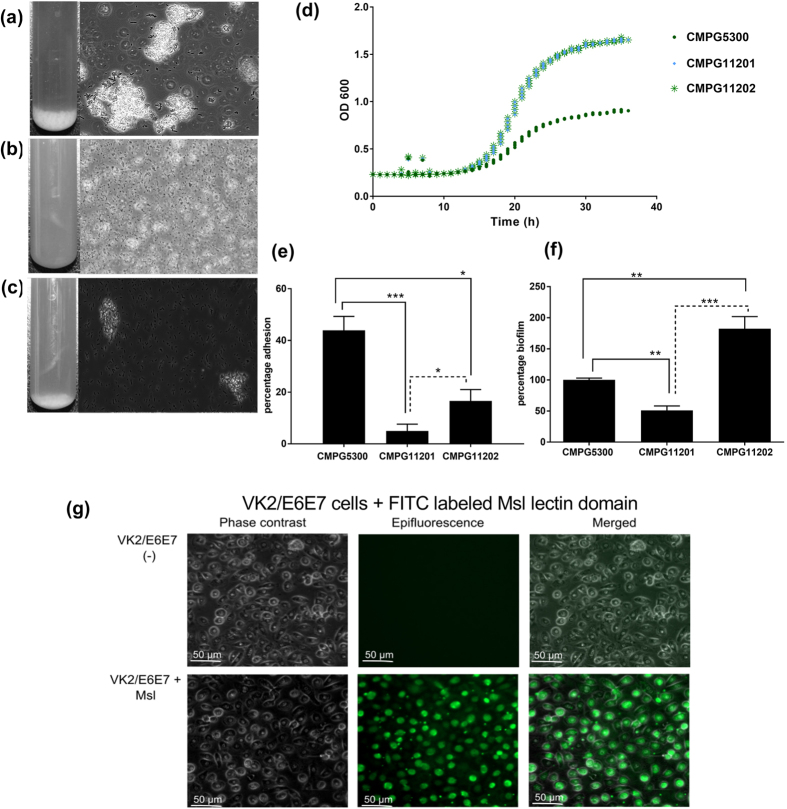
Figure 2. Phenotypic analysis of the mutant strain CMPG11201.
(a) Overnight cultures of L. plantarum CMPG5300 (b) its mutant CMPG11201, and (c) complemented strain CMPG11202 in MRS medium. Phase-contrast microscopic images show extensive cell clumps in the case of L. plantarum CMPG5300 (a) and some clumps in the complemented strain CMPG11202 (c), in contrast to the small-sized clusters and mostly single cells that are seen with the mutant CMPG11201 (b). (d) Growth capacity of L. plantarum CMPG5300, CMPG11201 and CMPG11202 mutants in MRS medium. (e) Adhesion capacities of L. plantarum CMPG5300 and CMPG11201 mutant to VK2/E6E7 vaginal epithelial cells. (f) Biofilm formation capacities of L. plantarum CMPG5300 and mutant CMPG11201. The results are expressed relative to the biofilm thickness of L. plantarum CMPG5300 wild-type (positive control), which was set at 100%. The error bars represent standard deviations of 8 biological repeats. The dataset comparisons (mutant pairwise to wild-type or complemented strain pairwise mutant strain) are considered significant (p < 0.05 indicated with one asterisks, p < 0.01 indicated with two asterisks and p < 0.001 indicated with three asterisks in the figure). (g) Binding of the FITC-labelled lectin domain of Msl to VK2/E6E7.