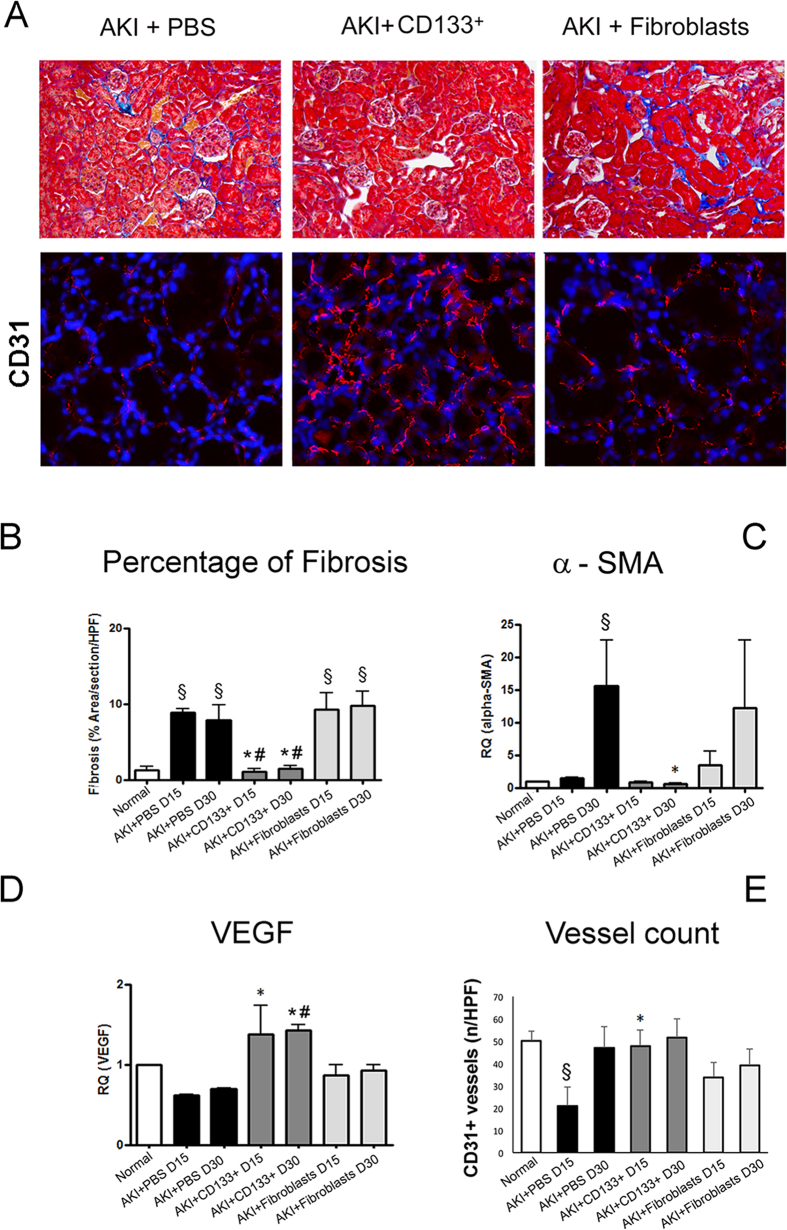
Figure 3. CD133+ cells protect against fibrosis and promote vascularization in AKI SCID model.
(A) Representative micrographs showing renal tissues of mice treated with PBS, CD133+ and dermal fibroblasts at day 15 after glycerol injection. Upper panels: Masson’s trichrome staining showing collagen in blue and erythrocytes in yellow. Lower panels: Immunofluorescence staining of CD31 positive vessels, shown in red. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Original magnification: upper panels: 200×; lower panel: 400×. (B) Quantification of fibrosis in normal and AKI mice performed by count of collagen area (blue colour) in the interstitium by Image J software on 10 fields/section in two sections/mouse. (C,D) qPCR analysis of whole kidney lysates of normal and AKI mice for α-SMA and VEGF. Data are mean ± SD of three independent experiments and are normalized to GAPDH mRNA and to 1 for normal and expressed as relative quantification (RQ). (E) Count of CD31+ structures of normal and AKI mice kidney tissue performed on 10 fields/section in two sections/mouse. ANOVA with Newman Keuls’ multicomparison test was performed: §p < 0.01 versus Normal; *p < 0.01 versus PBS, #p < 0.01 versus fibroblasts.