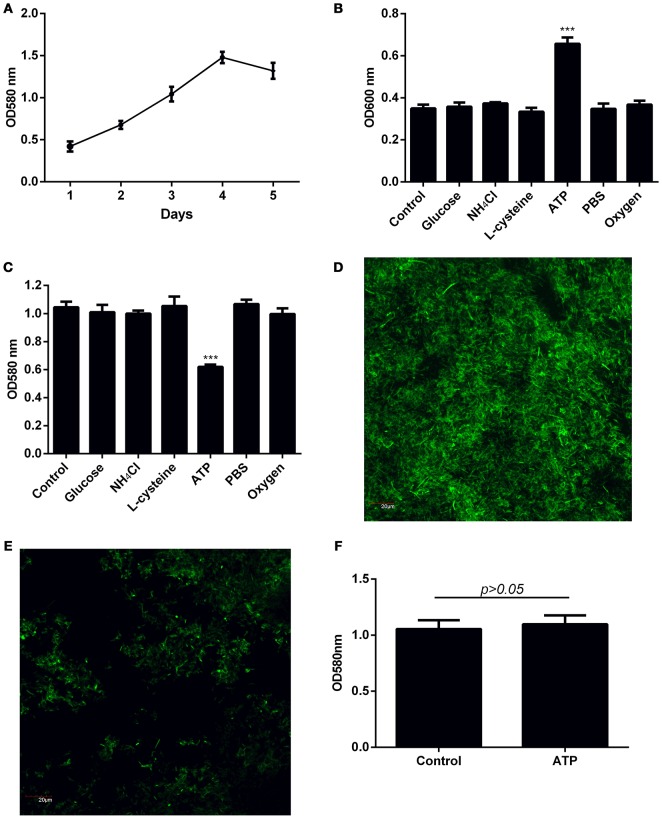
Figure 1.
Investigation of factors inducing dispersal of F. nucleatum biofilm. (A) The amount of biofilm formed over a 5-day period was quantified by crystal violet assay. (B) Four-day old F. nucleatum biofilm was left untreated (control) or treated with 2 mM D-glucose, 20 mM NH4Cl, 8 mM L-cysteine, 1 mM ATP or PBS, and incubated anaerobically at 37°C for 1 h. A separate plate of 4-day old F. nucleatum biofilm was incubated at 37°C for 1 h aerobically (~20% atmospheric O2). The amount of dispersed bacteria was determined by measuring optical density of bacteria in the culture supernatant. (C) The amount of biofilm biomass after induction of dispersal was quantified by crystal violet assay. Biofilm grown on cover slips in 24 well plates was left (D) untreated or (E) treated with ATP for 1 h. The amount of remaining biofilm was visualized by CLSM following staining with SYTO 9. Magnification 60X, scale bar: 20 μm. (F) F. nucleatum biofilm was cultured in the presence of 1 mM ATP for 4 days with daily change of media. The amount of biofilm formed was quantified by crystal violet assay. The data presented were obtained from one representative experiment carried out in triplicate. All experiments were performed 3 independent times and showed similar trends (Supplementary Figure 1). ***p < 0.001.