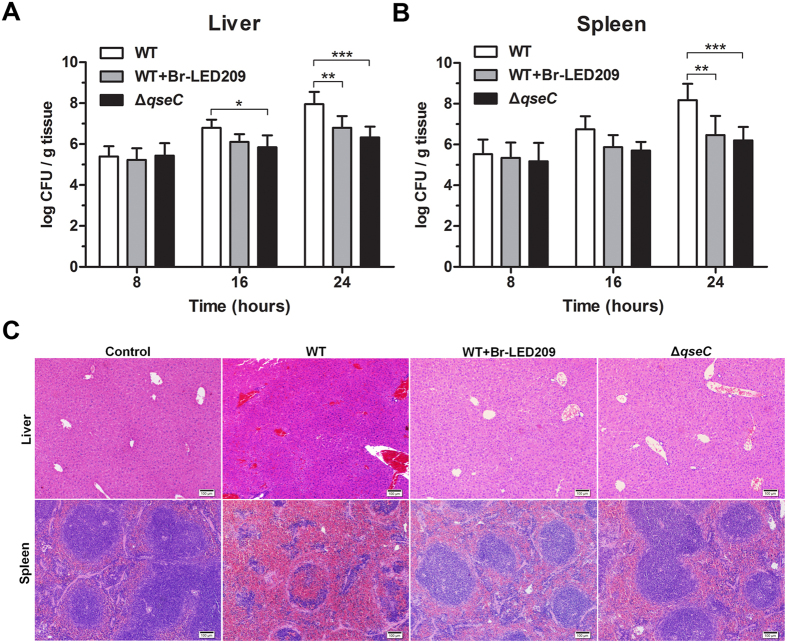
Figure 2. Bacterial burden and pathological damages in organs of infected mice were reduced by blocking QseC.
(A,B) BALB/c mice were infected by intraperitoneal administration of 1.0 × 108 CFUs of WT S. Typhimurium or the qseC mutant. The mice were treated twice orally with Br-LED209 (20 mg/kg) at 3 h before and after infection. Livers and spleens were harvested at 8, 16 and 24 hours after infection, homogenized and then plated on agar plates for bacterial counts. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. WT in two-way ANOVA, n = 5) (C) Morphological characteristics of liver and spleen in BALB/c mice were compared among groups infected with WT S. Typhimurium, the qseC mutant or Br-LED209. Scale bars: 100 μm.