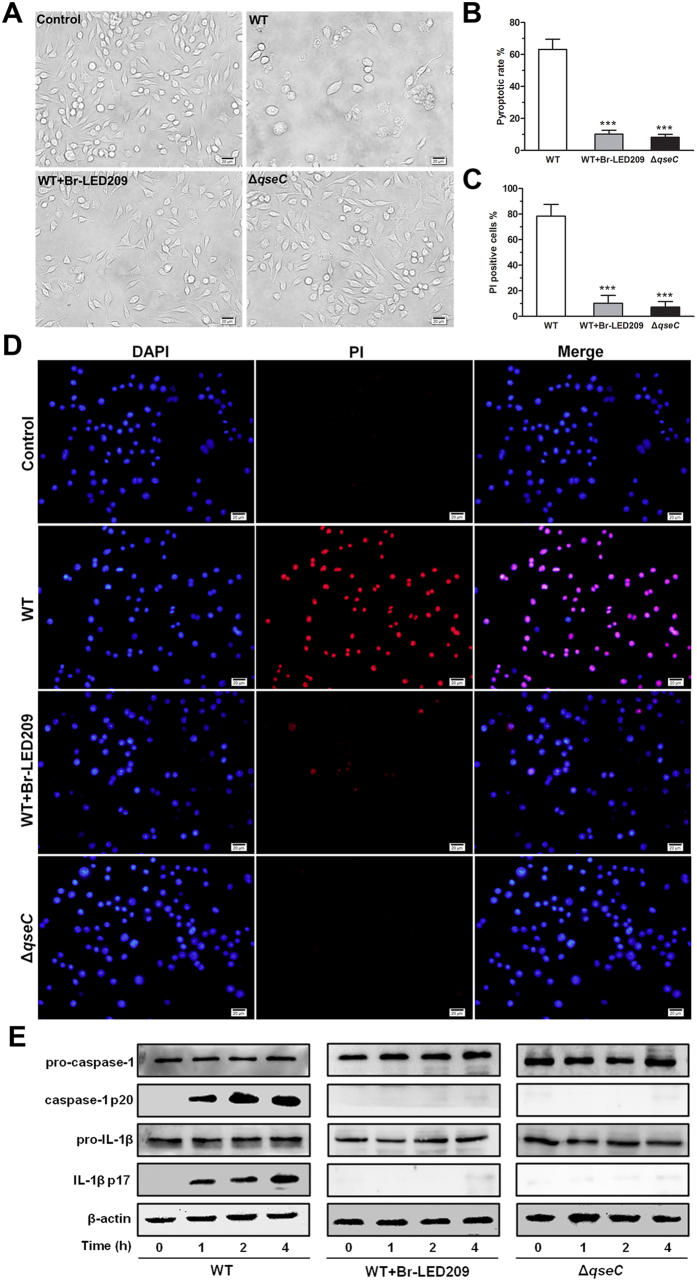
Figure 5. Inflammasome activation and pyroptosis of infected macrophages was inhibited by blocking QseC.
(A) S. Typhimurium were grown overnight in LB and subsequently diluted at 1:50 into fresh LB and grown for 3-4 h at 37 °C. Macrophages were infected with WT S. Typhimurium or the qseC mutant diluted in fresh DEME at MOI of 25:1. Morphological characteristics of macrophages after S. Typhimurium infection. Light microscope images were taken at 1 hour post-infection. Scale bars: 20 μm. (B) LDH released from S. Typhimurium-infected macrophages was measured. The pyroptotic rate of macrophages was calculated based on the equation in methods. (***P < 0.001 vs. WT in one-way ANOVA, n = 3) (C,D) Membrane permeability of macrophages after S. Typhimurium infection. Macrophages were stained with DAPI and the membrane impermeant dye propidium iodide (PI). Scale bars: 20 μm. The percentage of PI-positive cells was determined by counting cell numbers in four random visual fields. (***P < 0.001 vs. WT in one-way ANOVA) (E) Macrophages were infected with S. Typhimurium. Activated caspase-1 and IL-1β were precipitated from macrophage supernatants and detected by Western blot.