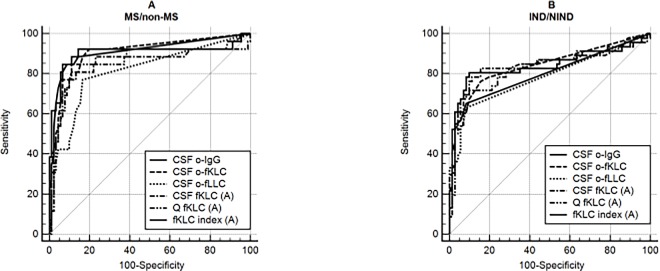
Fig 2. ROC curves in the context of MS and IND diagnoses.
a. MS versus non-MS b. Inflammatory neurological diseases versus non-inflammatory neurological diseases and symptomatic controls a. 26 MS and 91 non-MS patients were compared. AUCs for o-IgG, o-fKLC, o-fLLC, CSF fKLC, Q fKLC and fKLC index were 0.911, 0.907, 0.813, 0.850, 0.857 and 0.903, respectively. Significant differences were found between o-IgG and o-fLLC (P = 0.0035), o-fKLC and o-fLLC (P = 0.0075), fKLC index and Q fKLC (P = 0.0031), o-fKLC and CSF fKLC (P = 0.0201), o-fKLC and Q fKLC (P = 0.0219), fKLC index and CSF fKLC (P = 0.0347). Differences between o-IgG and Q fKLC (P = 0.0477), o-IgG and CSF fKLC (P = 0.0700), and fKLC index and o-fLLC (P = 0.0474) were of borderline significance. Other differences were not significant. b. 46 inflammatory neurological diseases (IND) and 71 non-inflammatory neurological diseases and symptomatic controls (NIND) patients were compared. AUCs for o- IgG, o-fKLC, o-fLLC, CSF fKLC, Q fKLC and fKLC index were 0.798, 0.840, 0.783, 0.838, 0.825 and 0.840, respectively. Although the AUCs for o-fKLC and fKLC index are slightly larger than for o-IgG, the only significant difference was observed between o-fKLC and o-fLLC (P = 0.0299). Quantitative measurements by the method (A) (Freelite™on SPAPLUS) were considered for these comparisons.