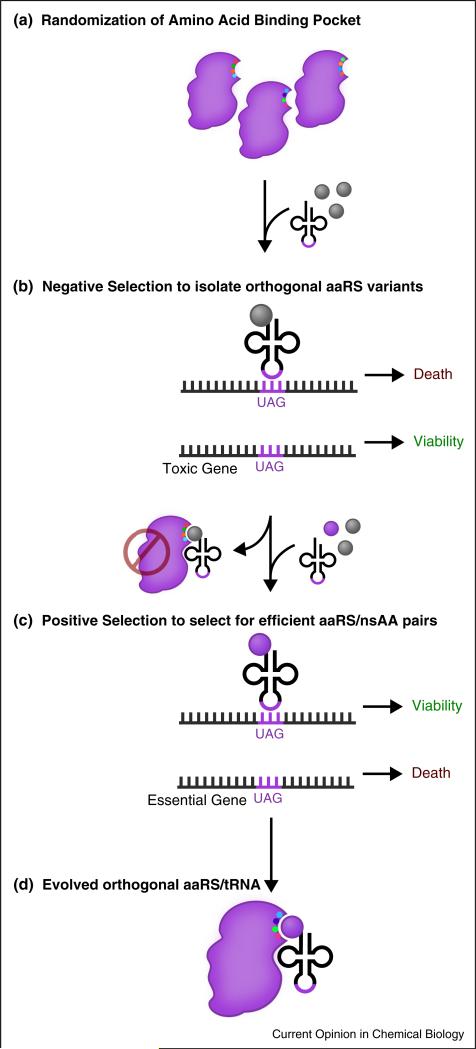
Figure 2.
General methodology for engineering orthogonal translation systems for novel nsAAs. (a) Scaffold orthogonal aaRS/tRNA pairs are selected from distant organisms. Residues in the amino acid binding pocket of the aaRS are randomized. (b) A negative selection is performed to exclude aaRS variants capable of charging natural amino acids. In the absence of the nsAA, clones are selected by the inability to suppress a toxic gene. (c) A positive selection is performed to retrieve aaRS variants capable of charging the nsAA, selecting for the ability to suppress a selectable marker gene, such as an antibiotic resistance marker. (d) The selected orthogonal translation system consists of the orthogonal aaRS, tRNA, and nsAA.