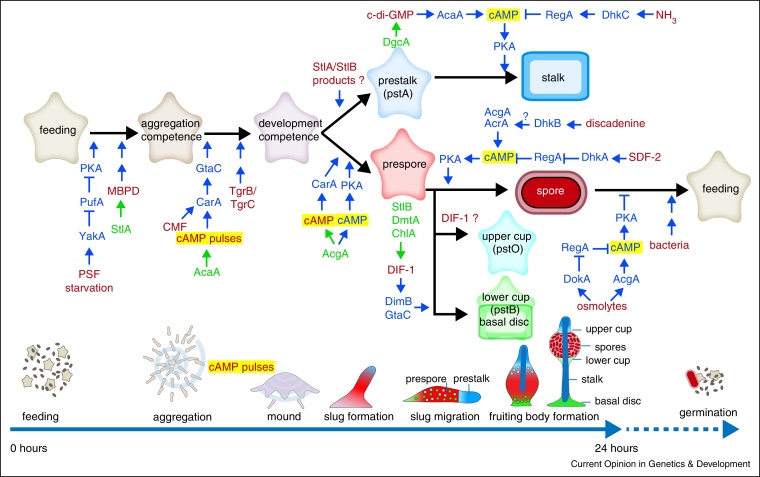
Figure 1.
Developmental signalling during the D. discoideum life cycle. During their 24 h life cycle, starving amoebas aggregate by secreting and relaying cAMP pulses to form multicellular mounds. The mound tip continues to emit cAMP pulses attracting cells from underneath, which push the tip upwards to form a slug. In the slug cells differentiate into precursors of spore and stalk, basal disc and upper and lower cup cells. Upon initiation of fruiting body formation, tip cells differentiate into stalk cells and move downwards. Most remaining cells move up the stalk and differentiate into spores and upper and lower cup cells. Cells that remain on the substratum differentiate into a basal disc. Stalk and basal disc cells share a similar highly vacuolated phenotype with a cellulose wall, while spores have condensed cytosol and a three-layered cellulosic wall that is also protein-rich. The environmental and secreted signals that control these life cycle transitions and the differentiation of amoebas are shown in red, with processes regulated by cAMP highlighted in yellow. The enzymes that synthesize secreted signals are shown in green, while proteins and small molecules that mediate intracellular signal processing are shown in blue. Blue arrows and t-crosses denote stimulatory and inhibitory effects, respectively, while double blue arrows signify that the mode of action of the signal is unknown. Abbreviations: AcaA: adenylate cyclase A; AcgA: adenylate cyclase G; AcrA: adenylate cyclase R; cAMP: 3′-5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CarA: cAMP receptor 1; c-di-GMP: 3′,5′-cyclic diguanylic acid; ChlA: flavin-dependent halogenase Chlorination A; CMF: conditioned medium factor; DgcA: diguanylate cyclase A; DhkA: histidine phosphatase A; DhkB: histidine kinase B; DhkC: histidine kinase C; DIF-1: differentiation inducing factor 1; DimB: transcription factor DIF-insensitive mutant A; DmtA: des-methyl-DIF-1 methyltransferase; DokA: osmosensing histidine phosphatase; GtaC: GATA-binding transcription factor C; MBPD: 4-methyl-5-pentylbenzene-1,3-diol; NH3: ammonia; PKA: cAMP-dependent protein kinase; PSF: prestarvation factor; PufA: pumilio RNA binding protein; RegA: cAMP phosphodiesterase with response regulator; SDF-2: spore differentiation factor 2; StlA: polyketide synthase Steely A; StlB: polyketide synthase Steely B; Tgr: transmembrane, IPT, IG, E-set, repeat protein; YakA: DYRK family protein kinase.