Table 1.
T-cell-mediated ADR classification, pathogenesis and phenotype guide
| Type IV ADR | Cellular mediators | Cytokine mediators | Phenotype | Specific immunological parameters for phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type IVa |
Primary: Th1 Secondary: Macrophages |
IFN-y TNF-a IL-18 |
Contact dermatitis Tuberculin reactions |
Contact dermatitis – Primarily CD8+ T cell infiltrate.
 IFN-y, TNF-a, IL-18. Also noted IFN-y, TNF-a, IL-18. Also noted
 lL-31, IL-6 in serum and IL-33 IL-9, IL-4 in skin [14–18]. lL-31, IL-6 in serum and IL-33 IL-9, IL-4 in skin [14–18]. |
| Type IVb |
Primary: Th2 Secondary: B-cells, IgE, IgG4, mast cells, Eosinophils |
IL-4 IL-5 IL-13 |
MPEa
HSS DRESS |
MPE – CD4 > CD8+ T cells. Acute episodes Th1 predominate,
 IL-12, IFN-y/TNF-b in blood, CXCL9/CXCL10 skin. IL-12, IFN-y/TNF-b in blood, CXCL9/CXCL10 skin.
 IL-17 compared with SJS/TEN. IL-17 compared with SJS/TEN.
 Th2/IL-5 later explains pruritis [19–24]. Th2/IL-5 later explains pruritis [19–24].DRESS -  TNF-a, IFN-y and IL-2 production, production correlates with disease severity. Activation-regulated chemokine (TARC/CCL17) drive Th2 responses, higher than observed in SJS/TEN. Skin biopsies noted eosinophils in 20%; whilst CD8+ T cells and granzyme B(+)lymphocytes TNF-a, IFN-y and IL-2 production, production correlates with disease severity. Activation-regulated chemokine (TARC/CCL17) drive Th2 responses, higher than observed in SJS/TEN. Skin biopsies noted eosinophils in 20%; whilst CD8+ T cells and granzyme B(+)lymphocytes
 in severe disease [25–27]. in severe disease [25–27]. |
| Type IVc | Primary: Cytotoxic T cells | Granzyme B Perforin Fas ligand Granulysin |
SJS TEN Linear IgA disease DILIb * FDE * EM |
SJS/TEN – CD8+ T-cells and NK cells lead to keratinocyte apoptosis. Granulysin specific to SJS/TEN.
 IL-10 and Treg associated with resolution of TEN/SJS. Treg function often impaired. IL-10 and Treg associated with resolution of TEN/SJS. Treg function often impaired.
 IL-2, IL5, IL6, IL-17 and CCL27 in plasma/blister fluid. Th17 cells also have a role [23,28–35]. IL-2, IL5, IL6, IL-17 and CCL27 in plasma/blister fluid. Th17 cells also have a role [23,28–35].Linear IgA disease – Often mistaken for TEN, however characteristic linear IgA deposits are evident on direct immunofluorescence studies.  CD4+ T-cell, neutrophils and eosinophilis. Mixed Th1/Th2 cytokine response. CD4+ T-cell, neutrophils and eosinophilis. Mixed Th1/Th2 cytokine response.
 IL-2, IL-4, IL-5 and IL-8 noted [36–41]. IL-2, IL-4, IL-5 and IL-8 noted [36–41]. FDE –  Intraepidermal CD8+ T-cells, Intraepidermal CD8+ T-cells,
 IFN-y, cytotoxic granules, granzyme B and perforin. IFN-y, cytotoxic granules, granzyme B and perforin.
 CD8+ T-cells, CD4+ T-cells and neutrophils cause tissue damage. Late - CD8+ T-cells, CD4+ T-cells and neutrophils cause tissue damage. Late -
 IL-10 & Treg(CD4+CD25+Foxp3+) control immune reaction, however IL-15 secreted by keratinocytes continue to propagate CD8+ T-cell mediated injury [42,43]. IL-10 & Treg(CD4+CD25+Foxp3+) control immune reaction, however IL-15 secreted by keratinocytes continue to propagate CD8+ T-cell mediated injury [42,43]. EM –  IL2, IL6, IL8, IL17A, IFN-y. IL2, IL6, IL8, IL17A, IFN-y.
 Th1/CD4+ T-cell infiltrate with IL-17 expression. Th1/CD4+ T-cell infiltrate with IL-17 expression.
 IL10, noted. At skin level, IL10, noted. At skin level,
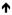 CD4+ T cell with IL-17 (Th2) expressing cells. CD8+ T cells noted within epidermis, and CD4+ T cells are noted in dermis. Variations in T-cell/cytokine expression if the stimulant is HSV or drug induced (e.g. higher CD8+ T cells and TNF-a in drug-induced EM) [44–46]. CD4+ T cell with IL-17 (Th2) expressing cells. CD8+ T cells noted within epidermis, and CD4+ T cells are noted in dermis. Variations in T-cell/cytokine expression if the stimulant is HSV or drug induced (e.g. higher CD8+ T cells and TNF-a in drug-induced EM) [44–46]. |
| Type IVd |
Primary: Th1/Th17 Secondary: Neutrophils |
GM-CSF IL-8 CXCL8 |
AGEP |
AGEP –
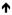 CD4+ T cells infiltrate, CD8+ T cells and CD4+ T cells infiltrate, CD8+ T cells and
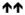 CXCL8 and GM-CSF. CXCL8 is involved in the chemotaxis of neutrophils; Th17 cells involved [47–50]. CXCL8 and GM-CSF. CXCL8 is involved in the chemotaxis of neutrophils; Th17 cells involved [47–50]. |
References:[13]
Abbreviations: Th1, Type 1 T helper cells, Th2, Type 2 T helper cells; Th17, Type 17 T helper cells; IL, interleukin; DHR, Drug hypersensitivity reaction; SJS, Stevens-Johnson syndrome; TEN, toxic epidermal necrolysis; MPE, maculopapular exanthema; DRESS, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms; HSS, hypersensitivity syndrome; FDE, fixed drug eruption; EM, erythema multiforme; DILI, drug induced liver injury; AGEP, acute generalised exanthematous pustolosis; GM-CSF, granulocyte monocyte colony-stimulating factor; PMN, polymorphonuclear cell.
Not classically described by Gell and Coombs criteria of T cell-mediated hypersensitivity
MPE, otherwise known as ‘morbilliform’ drug eruption, is the most commonly reported antibiotic-associated T-cell-mediated ADR.
DILI - DILI will not be covered in detail in this review, as the mechanism can be dose dependent/predictable or unpredictable. The unpredictable reactions may in fact be IM or metabolic in origin. T lymphocytes secreting granzyme B have been noted on liver biopsy. CD4+/CD8+ T cells secreting IL-13 and IFN-y have been detected in serum from in patients with DILI.. The most commonly implicated antimicrobials are amoxicillin-clavulanate and flucloxacillin, in particular in those with HLA-B*57:01
