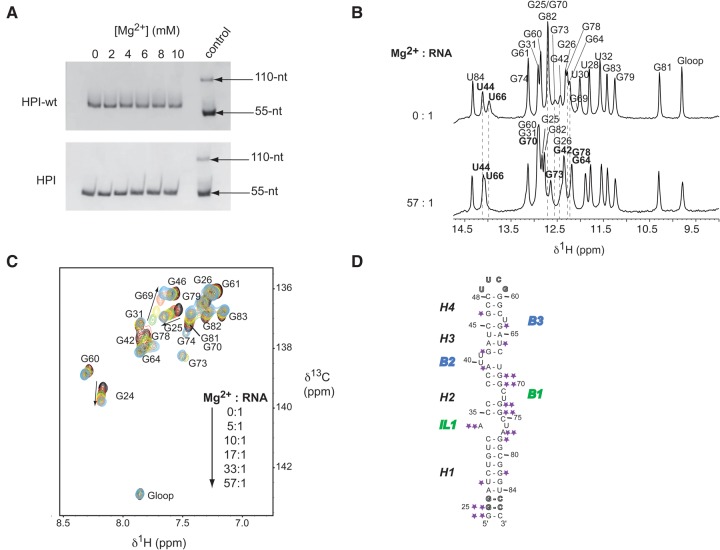
FIGURE 6.
Effect of magnesium on HPI. (A) Native gel electrophoresis on 10% polyacrylamide. HPI-wt (top) and HPI (bottom) were loaded in the buffer used for NMR studies with increasing magnesium concentration. The last lane (control) contains a thio-modified RNA at its 5′-end, which allows the visualization of a monomer (55-nt: S-RNA) and a dimer (110-nt: RNA-S-S-RNA). (B) Titration of HPI by magnesium by monitoring exchangeable protons. The assignment of imino protons based on the analysis of NOESY experiments is indicated for the Mg2+-free RNA (top) and the 10 mM Mg2+-RNA corresponding to a ratio of 57:1 (bottom). Broken lines and bold assignments indicate imino protons that undergo chemical shifts changes. (C) Magnesium titration of HPI using nonexchangeable protons. Overlays of regions of 1H–13C HSQC spectra showing the aromatic H8-C8 of selectively labeled [13C/15N-G] HPI at 30°C, Mg2+-free (black) and upon successive additions of magnesium. Arrows indicate the cross-peaks that shifted upon addition of magnesium. (D) Summary of the effects observed in 1H and 13C experiments on HPI upon Mg2+ binding. Small effects are indicated by one star, while stronger effects are highlighted using two stars.