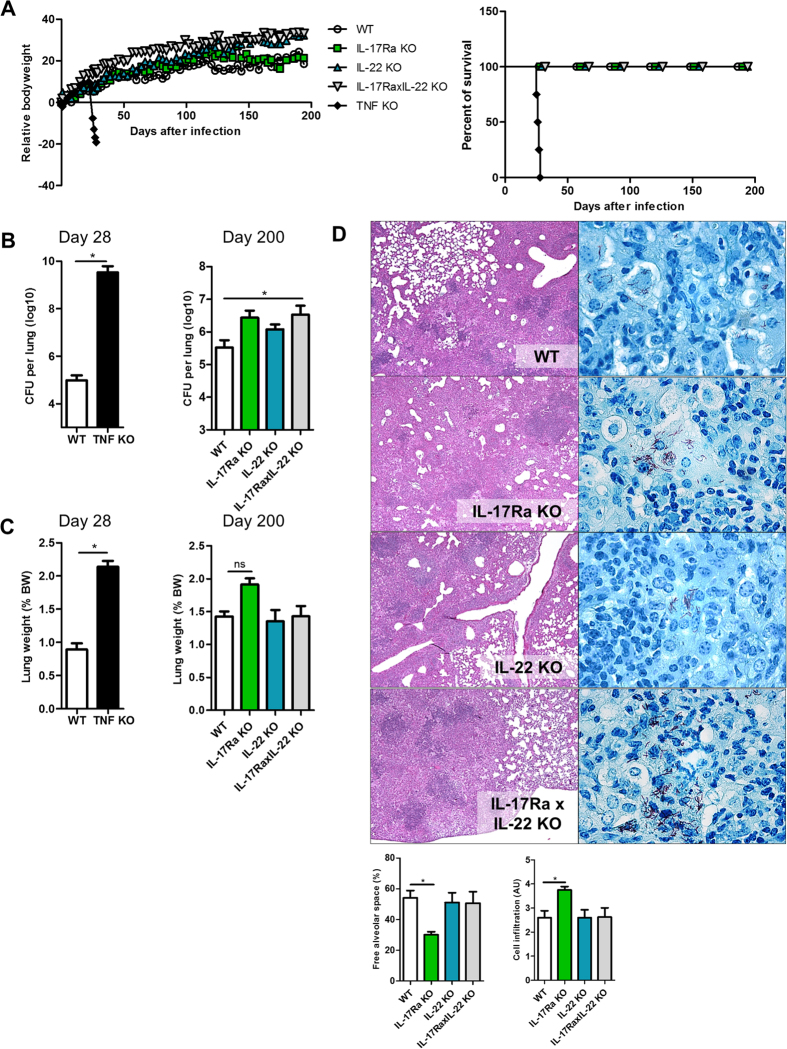
Figure 4. Contained chronic M. tuberculosis infection in the absence of IL-17RA and/or IL-22 pathways.
Mice deficient for IL-17RA, IL-22, both IL-17RA and IL-22, and TNFα mice as well as wild-type mice were infected with M. tuberculosis (H37Rv, 1000 CFU/mouse i.n.). Body weight and survival were monitored during 200 days (A). Pulmonary bacterial load (B) and lung relative weight (C) were measured 28 days post-infection for sensitive TNFα-deficient mice and 200 days post-infection for the IL-17RA- and/or IL-22-deficient mice. Lung pathology was assessed at 6 months (D). Macroscopically large, confluent nodules were visible in all groups. Microscopic examination showed extensive inflammation with limited free alveolar space (Left, haematoxylin and eosin, magnification ×50), with the presence of acid-fast bacilli (Right, Ziehl-Nielson, magnification ×1000). Histopathological score of free alveolar space and cell infiltration per group are indicated. Results are expressed as mean +/− SEM of n = 4–7 mice per group, *p < 0.05.