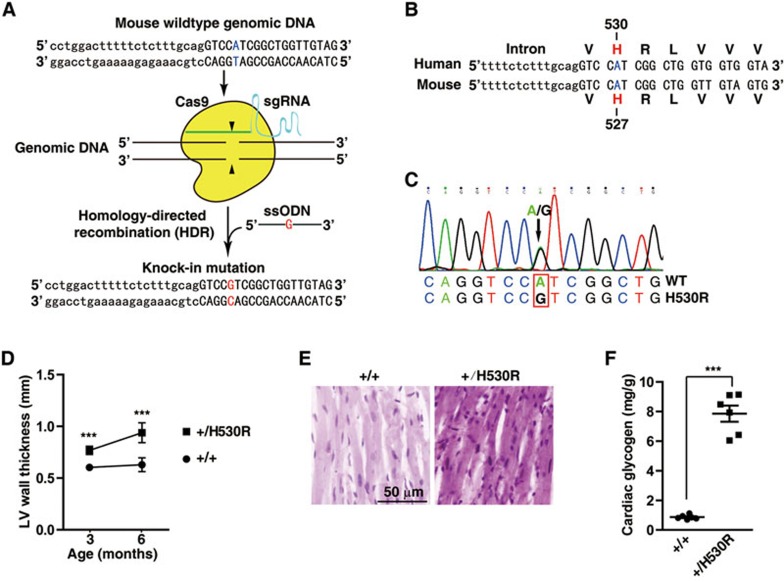
Figure 2.
H530R knock-in mice recapitulate the PRAKG2 cardiac syndrome. (A) Schematic showing the generation of H530R-PRKAG2 knock-in mouse model using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Lowercase characters denote the intronic region and uppercase characters denote the exonic region. (B) Alignment of genomic DNA and protein sequences of human and mouse PRKAG2 near the H530 locus. The H530 of human PRKAG2 is equivalent to H527 of mouse PRKAG2. The obtained knock-in mouse model is referred to as the H530R-PRKAG2 knock-in model. (C) Validation of heterozygous H530R knock-in mice by sequencing. (D) LV wall thickness calculated by continuous echocardiography. Data represent mean ± SD. Two-way ANOVA was performed for overall differences (n = 6). Unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test was performed for single comparison (***P < 0.001). (E) PAS staining of paraffin-embedded sections. (F) Measurement of glycogen content in hearts from 3-month-old WT (+/+) and heterozygous H530R knock-in (+/H530R) mice. Data represent mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA was performed for overall differences (n = 6). Unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test was performed for single comparison (***P < 0.001).