Figure 3.
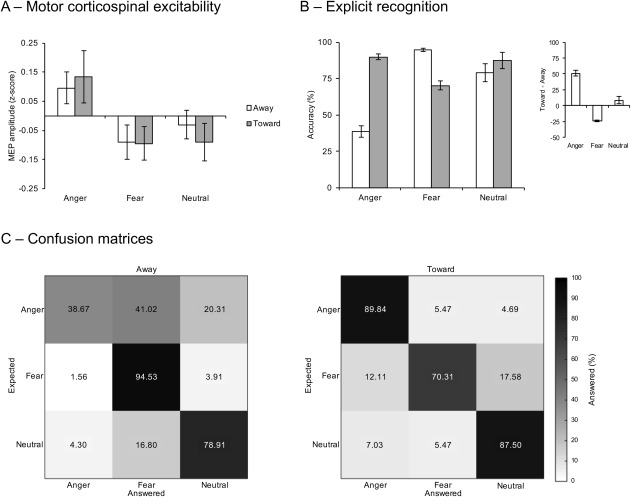
The effect of direction of threat on motor corticospinal excitability levels and explicit recognition accuracy. MEP amplitude did increase for anger independent of direction (A). Recognition accuracy was higher for angry expressions directed toward the observer and fear expressions directed away from the observer (B). Inset shows the incongruence effect. Anger directed away was confused with fear, while no clear confusion was observed for fear directed toward the observer (C).
