Figure 3.
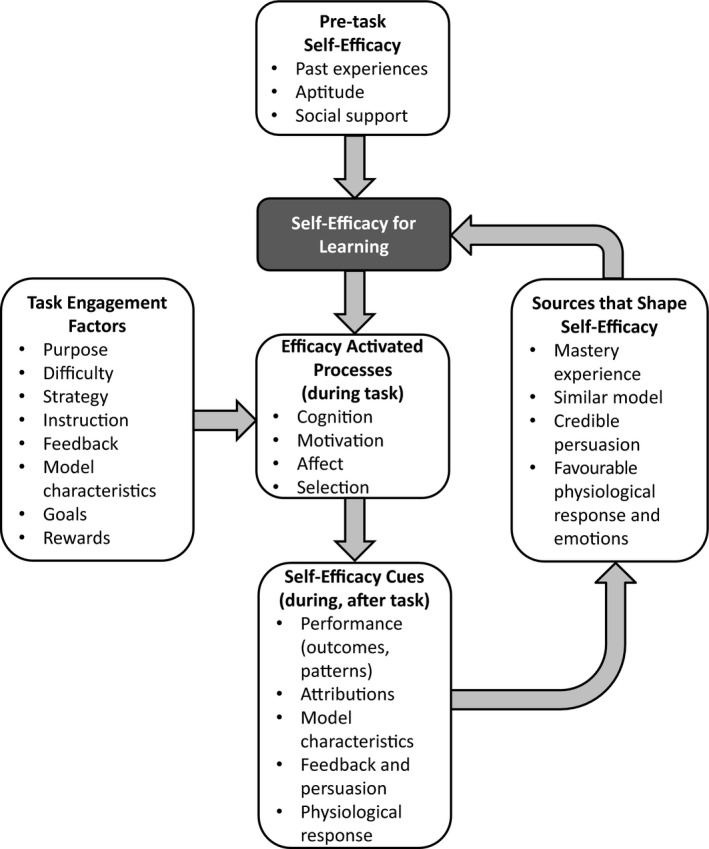
Social‐cognitive model of motivated learning. This is adapted from Schunk's model of motivated learning; it incorporates additional concepts from Bandura and other authors. Learners begin a learning task with pre‐existing self‐efficacy determined by past experiences, aptitudes and social supports. Learners can perform the task themselves or watch others (e.g. instructor or peer models) perform the task. During the task, self‐efficacy, together with other personal and situational factors, influences cognitive engagement, motivation to learn, emotional response and task selection. During and after the task, learners perceive and interpret cues that influence self‐efficacy for future tasks. Zimmerman defined a three‐phase self‐regulation cycle that mirrors this model, comprised of forethought (pre‐task), performance and volitional control (during task) and self‐reflection (after task)
