Figure 2.
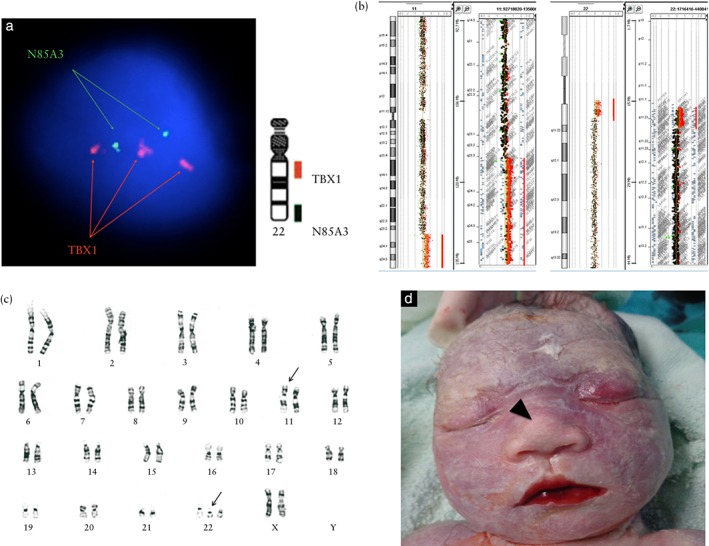
Genetic analysis of 35‐week fetus with multiple structural anomalies. (a) Interphase fluorescence in‐situ hybridization using DiGeorge TBX1/22q13.3 DNA probe (Cytocell, Inc., Cambridge, England) revealed TBX1 duplication in 90% (45/50) of amniocytes examined (nuc ish 22q11.2 (TBX1×3)). (b) Array comparative genomic hybridization using CytoScan gene chip (Agilent customer design ID 040427, Changhua Christian Hospital, Changhua, Taiwan) demonstrated two segmental duplications involving 11q23.3q25 (18.14 megabases (Mb)) (arr[hg19] 11q23.3q25(116,723,438‐134,868,407)×3) and 22q11.1q11.21 (3.21 Mb) (arr[hg19] 22q11.1q11.21(17,096,855‐20,311,763)×3). (c) Karyotype analysis of amniocytes revealed a suspect reciprocal translocation (47,XX,t(11;22)(q23;q11.2),+der(22)t(11;22)(q23;11.2)) (arrows). (d) The appearance of the terminated fetus was grossly normal except for a bulbous nose (arrowhead).
