Fig. 5.
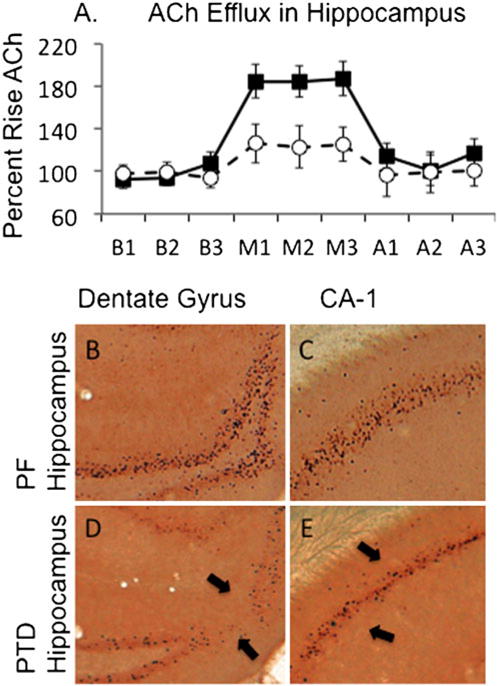
Behaviorally relevant acetylcholine (ACh) efflux in decreased in PTD rats (open circles) relative to control pair-fed (PF; closed squares) rats (a). Note that baseline levels (B1–B3) or after-maze levels (A1–A3) of ACh efflux are not different across the groups; the difference emerges only when the rats are tested for spontaneous alternation on the plus maze (M1–M3). In addition, relative to PF rats (b, c), behaviorally activated levels (induced by spontaneous alternation testing) of the early immediate gene c-Fos are decreased in PTD rats (d, e). The arrows point to the reduction of c-Fos positive cells with in the dentate gryrus and CA1 sector
