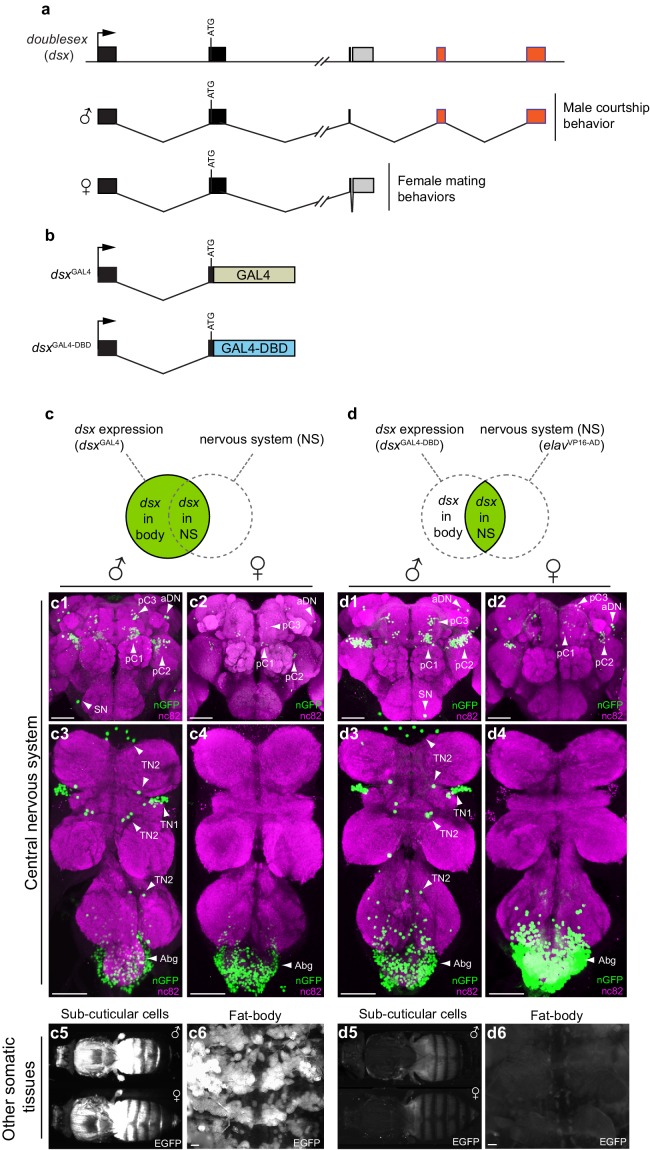
Figure 1. Spatial restriction of GFP expression to dsx neurons using novel dsx Split-GAL4 allele.
(a) Schematic of doublesex (dsx) gene and male and female predicted transcripts. Arrows indicate transcriptional start sites. Colored boxes depict non-sex-specific (black) and sex-specific (red: male and grey: female) exons. (b) Schematic of dsxGAL4 and dsxGAL4-DBD knock-in alleles. (c) GFP expression in five day-old males and females driven by dsxGAL4. (c1–4) dsxGAL4 driving UAS-nuclear GFP (nGFP) in (c1) adult male brain and (c3) VNC and (c2) adult female brain and (c4) VNC. (c5–6) Epifluorescence images of dsxGAL4 driving UAS-2XEGFP (EGFP) in (c5) adult male and female whole-fly preparations revealing EGFP expression in sub- and peri-cuticular cells and (c6) adult male filleted dorsal abdominal wall revealing EGFP expression in the adult fat body. (d) GFP expression in five day-old males and females driven by dsxGAL4-DBD combined with pan-neuronal elavVP16-AD hemidriver. (d1–4) dsxGAL4-DBD/elavVP16-AD (referred to as dsx/elav in text) driving UAS-nGFP in (d1) adult male brain and (d3) VNC and (d2) adult female brain and (d4) VNC. Epifluorescence images of dsxGAL4DBD/elavVP16-AD driving UAS-2XEGFP in (d5) adult male and female whole-fly preparations revealing no EGFP expression in sub- and peri-cuticular cells and (d6) adult male filleted dorsal abdominal wall revealing no EGFP expression in the adult fat body. nGFP realized with anti-GFP antibody (green) and neuropil counterstained with nc82 (magenta). EGFP realized with anti-GFP antibody (white). (c1–4) and (d1–d4) views are ventral, with anterior up. Scale bar = 50 μm.