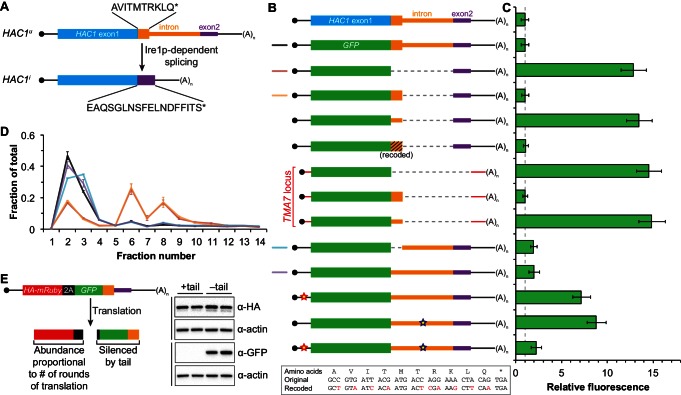
Figure 3. Post-translational silencing mediated by the intron-encoded C-terminal tail.
(A) Schematic of HAC1 mRNA splicing. The proteins encoded by HAC1u and HAC1i mRNAs differ in their C-terminal tails, with the amino acid sequences indicated. (B) Design of reporter mRNAs. Black shading indicates recoding, with the original and recoded sequences depicted below (mutations in red). Untranslated regions colored red correspond to those of the TMA7 mRNA, with the reporter gene integrated at the TMA7 rather than HAC1 locus. Otherwise constructs are depicted as in Figure 2B. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of reporter strains. Strains expressing the GFP reporter mRNAs depicted in (B) were analyzed as in Figure 2C, with data for the first three strains duplicated from Figure 2B for comparison. (D) Polysome analysis of reporter mRNAs. Extracts were prepared in heparin-containing lysis buffer from strains expressing the GFP reporter mRNAs indicated in (B). Polysome analysis was performed as in Figure 1A, with data for the wild-type and intronless GFP reporters from Figure 2A duplicated for comparison. (E) Differentiating between co-translational and post-translational silencing mechanisms. Left: Schematic of reporter construct that generates two separate polypeptides from each round of translation. Right: Extracts were prepared from strains expressing reporter mRNAs that either encoded the 10-amino-acid C-terminal tail of Hac1up (+tail) or contained a stop codon just before the tail (–tail). Immunoblotting was used to detect HA-tagged mRuby (top) and GFP (bottom), with actin as a loading control. Two biological replicates are shown for each genotype.
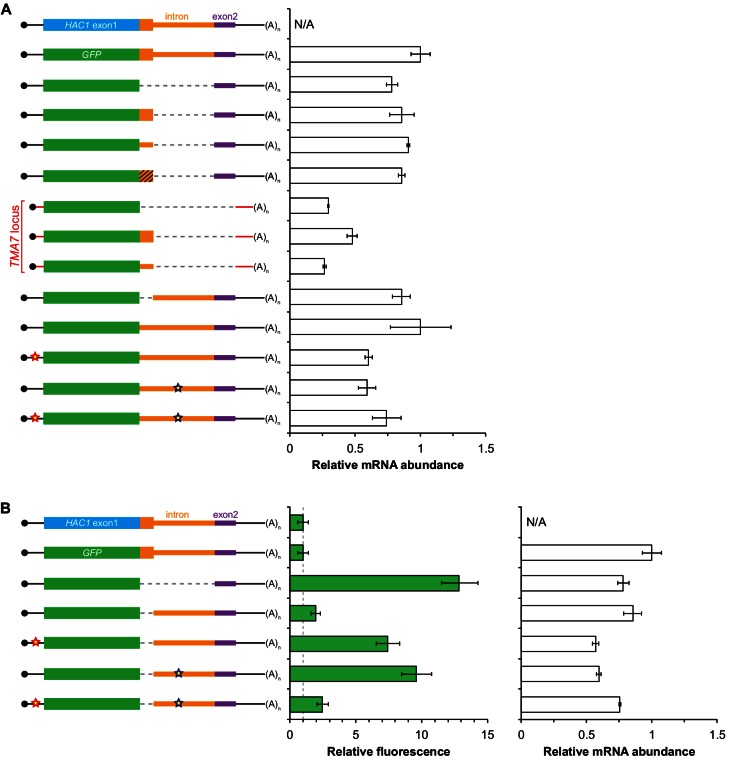
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Additional analyses of GFP reporter constructs.
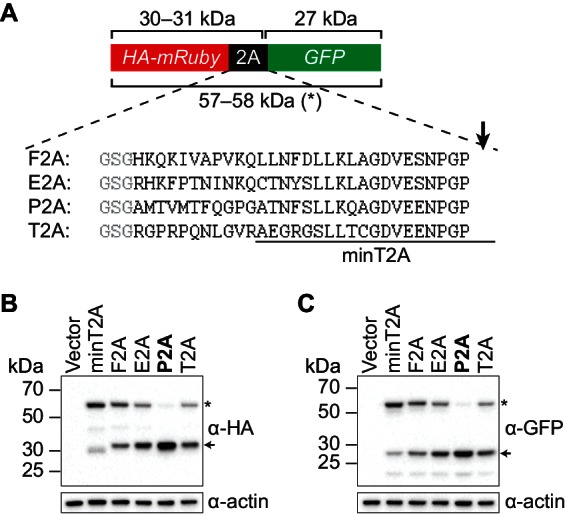
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Identifying a 2A peptide sequence that is active in S. cerevisiae.