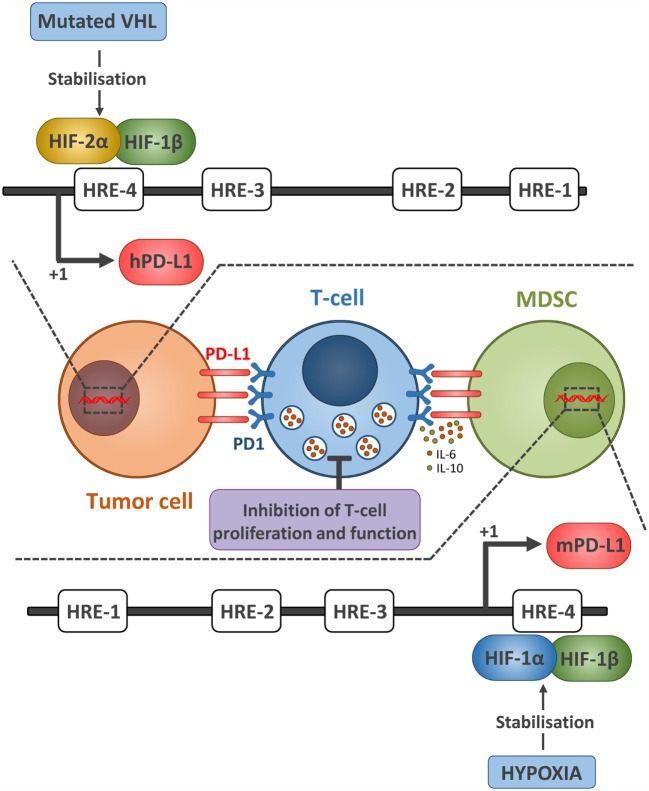
Figure 2.
Hypoxia via HIF-1α and HIF-2α regulates the expression of PD-L1 expression on tumor cell and MDSCs. The upper part represents the mechanism by which HIF-2α regulates the expression of PD-L1 in ccRCC tumor cells. Due to mutated VHL in ccRCC tumors, HIF-2α is constitutively stabilized and activated. HIF-2α translocates to the nucleus, binds to the HRE-4 in human PD-L1 promoter, and upregulates its expression. Whether this PD-L1 confers resistance to ccRCC sensitivity to antitumor effector cells remains to be investigated. The lower part represents the mechanism by which hypoxia via HIF-1α regulates the expression of PD-L1 in MDSCs. Similarly, stabilized HIF-1α in MDSCs isolated from tumors bound directly to the HRE-4 in the PD-L1 proximal promoter in MDSCs. The immune suppressive function of MDSCs, enhanced under hypoxia, was abrogated following PD-L1 blockade and hypoxia-mediated upregulation of IL-6 and IL-10 in MDSCs was significantly attenuated after PD-L1 blockade.