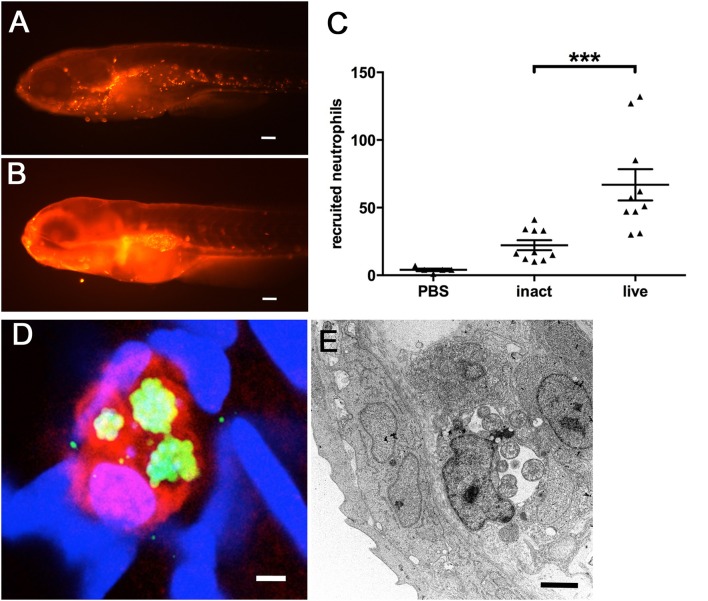
Figure 6.
Neutrophil recruitment and uptake of W. chondrophila monitored in transgenic Tg(lyzC:dsRednz50) larvae at 8 hpi. Whilst the swim bladder of a healthy larva is usually nearly devoid of innate immue cells (A), the injection of W. chondrophila into the swim bladder activates strong neutrophil recruitment (B). Quantification of recruited neutrophils (C) shows a significantly increased reaction to live W. chondrophila (live) compared to heat-inactivated (inact) bacteria or with sterile PBS injected control larvae, ***p < 0.001. After the uptake by a neutrophil W. chondrophila can successfully avoid its degradation and instead start replicating inside the phagosome to form an inclusion shown by 3D-CLSM (D) and TEM (E). (D) shows a 3D acquired z-stack image of a dsRed expressing neutrophil (red) of the transgenic Tg(lyzC:dsRednz50) line, harboring three W. chondrophila inclusions, visualized by antibody staining (green). DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). The TEM image in (E) shows a zebrafish phagocyte containing two inclusions of replicating W. chondrophila RBs. Scale bars (A,B) 100 μm, (D) 1 μm and (E) 2 μm.