FIGURE 2.
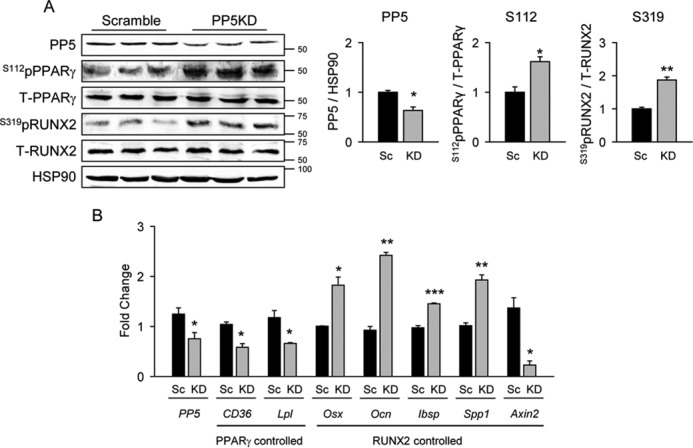
PP5 knockdown increased PPARγ and RUNX2 phosphorylation leading to increased PPARγ and reduced RUNX2-specific transcriptional activity. A. to achieve stable knockdown of PP5 protein expression, U-33/γ2 cells were infected with lentiviral constructs encoding either scrambled (Sc) or PP5-specific (KD) shRNA. Whole cell extracts were analyzed by Western blot with antibodies specific to Ser(P)-112 of PPARγ, or Ser(P)-319 of RUNX2 and antibodies against total PPARγ and RUNX2. HSP90 protein levels served as a loading control. Graphs represent densitometry analysis of Western blots (n = 6). Signals from bands representing phosphorylated proteins were normalized to signals from total proteins. B, the effect of PP5 silencing in U-33/γ2 cells on expression of gene markers controlled by either PPARγ or RUNX2 transcriptional activities (n = 6). Graphs represent -fold change in expression of analyzed markers in KD as compared with scrambled conditions. All transcripts expression was normalized to 18S RNA. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
