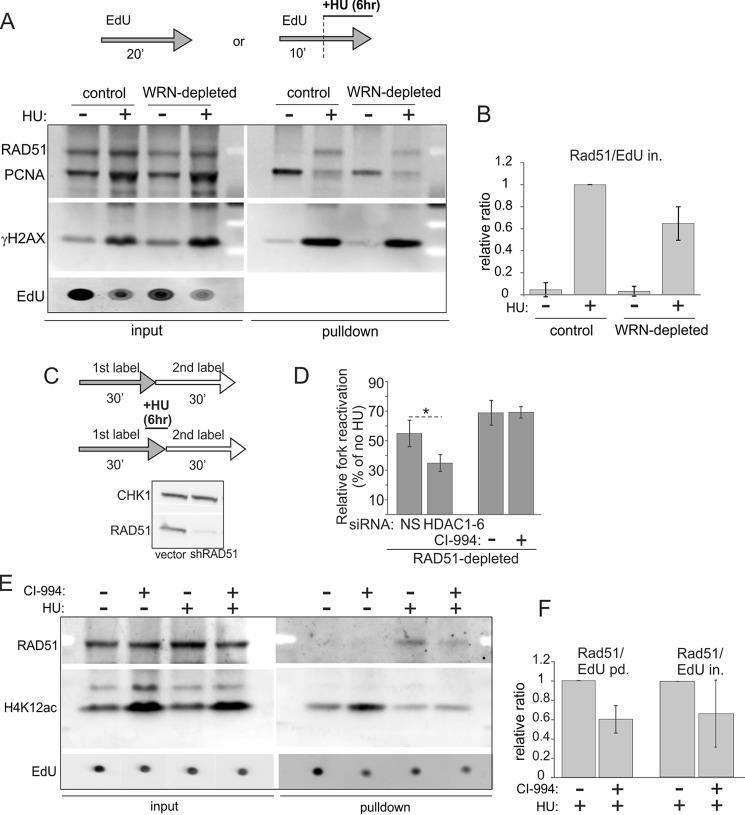
FIGURE 9.
RAD51 recruitment to HU-stalled forks is reduced by depletion of WRN or inhibition of histone deacetylase activity of HDACs 1, 2, and 3. A, iPOND measurement of levels of RAD51, PCNA, and γH2AX in mock-depleted and WRN-depleted GM639cc1 fibroblasts pulse-labeled with EdU and treated with 2 mm HU as indicated. B, quantitation of two independent experiments performed as in A. Levels of RAD51 in pulldown assays were normalized to EdU levels in input samples (EdU in.) as in Fig. 8, B and C. Normalized RAD51 levels in HU-treated control cells were set as the baseline, and the rest of the values were expressed relative to it. C and D, maRTA analysis of RAD51-depleted GM639cc1 fibroblasts labeled with EdU and IdU as 1st and 2nd labels, respectively, and treated with 2 mm HU as indicated. C, maRTA labeling scheme and a Western blot of RAD51 depletion in GM639cc1 cells. CHK1 is the internal control. D, a bar graph of relative fork reactivation, derived as in Fig. 3C from two replicate experiments with 500–800 track measurements per sample in each experiment. Significance was determined in a one-tailed t test (*, p = 0.035). E, iPOND measurement of RAD51 and H4K12ac recruited to replication forks in mock-depleted GM639cc1 fibroblasts treated with 3 μm CI-994 overnight before and during the experiment. 2 mm HU addition and EdU pulse-labeling are as in A. F, quantitation of two independent iPOND experiments performed as in E. Quantitation and plotting are as in B, except RAD51 levels in pulldown assays were normalized to EdU levels in pulldown assays (EdU pd., lanes 1 and 2) or in inputs (EdU in., lanes 3 and 4) for comparison.