FIGURE 1.
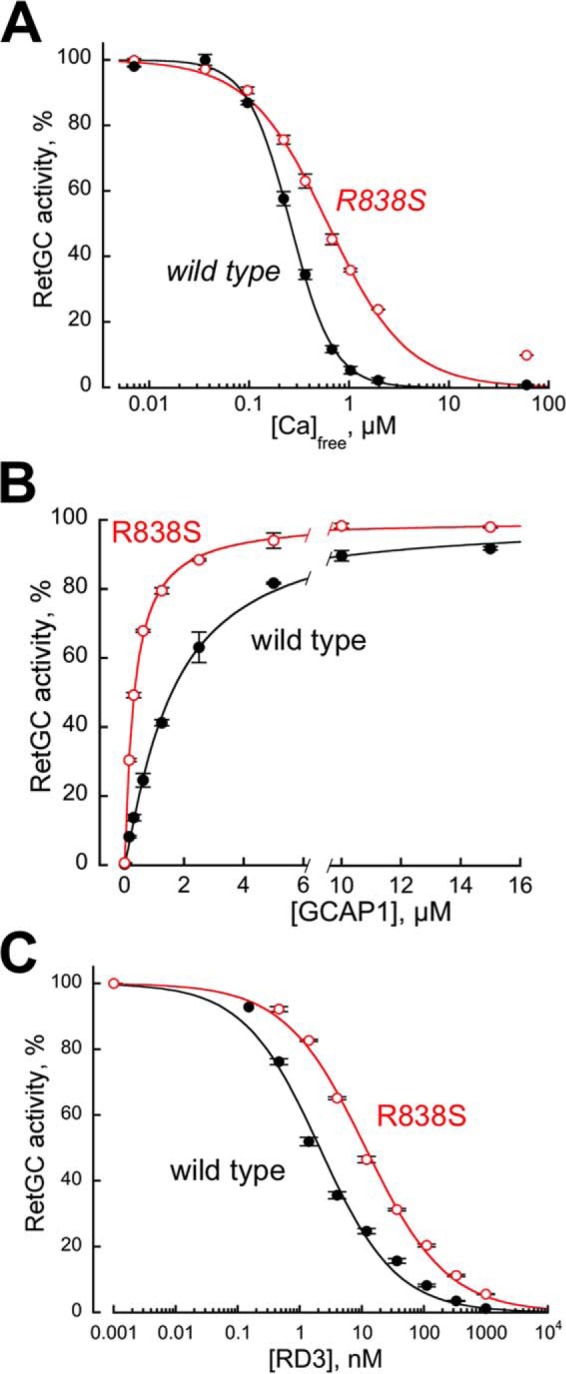
Altered biochemical characteristics of a recombinant CORD6 R838S RetGC1. RetGC1 was expressed in HEK293 cells and tested in vitro prior to making it into the transgene-expression construct. A, the calcium sensitivity of wild type (closed symbols) and R838S (R838S+, open symbols) RetGC1. The cyclase activity was assayed at varied concentrations of free Ca2+ set by Ca2+/Mg2+/EGTA buffers at a constant 0.9 mm free Mg2+. The data (mean ± S.D.) from two independent sets of experiments were normalized as the percentage of maximal activity in each cyclase preparation and fitted using the Hill function, A = (Amax)/(1 + ([Ca]/K½Ca)H), where Amax% is the respective maximal activity, [Ca] is the free Ca2+ concentration; K½Ca is the free Ca2+ concentrations causing 2-fold inhibition of the maximal activity, and H is the Hill coefficient. The respective K½Ca for wild type and R838S RetGC1 heterlogously expressed in HEK293 cells was 257 ± 14 and 610 ± 56 nm (p = 0.0051; here and further the p values are from Student's t test). B, the affinity of the R838S RetGC1 for its activator, Mg2+GCAP1, becomes drastically increased. The cyclase activity was assayed in the presence of 2 mm EGTA and saturating 10 mm MgCl2. The data were normalized in two independent experiments as %% of maximal activity in each case and fitted using the Hill function, A = Amax/(1 + ([GCAP1]/K½GCAP)−H), where [GCAP1] is the concentration of Mg2+ GCAP1, K½GCAP is the GCAP1 concentration required for the half-maximal stimulation, and H is the Hill coefficient. The K½GCAP1 for the wild type and R838S RetGC1 were 1585 ± 80 and 327 ± 10 nm, respectively (p < 0.03). C, activated R838S RetGC1 becomes more resistant to inhibition by RD3 protein. The cyclase assays were conducted in the presence of 2 mm EGTA, 10 mm MgCl2, 1.5 μm GCAP1, and varying concentrations of human recombinant RD3. The data from three independent sets of experiments were fitted using the Hill function, A = Amax/(1 + ([RD3]/K½RD3)H), where K½RD3 is the concentration of RD3 required for 50% inhibition of the RetGC1/GCAP1 complex activity. The K½RD3 for the wild type and the R838S RetGC1 were 2.6 ± 1.2 and 11.4 ± 0.4 nm, respectively (p < 0.01).
