FIGURE 3.
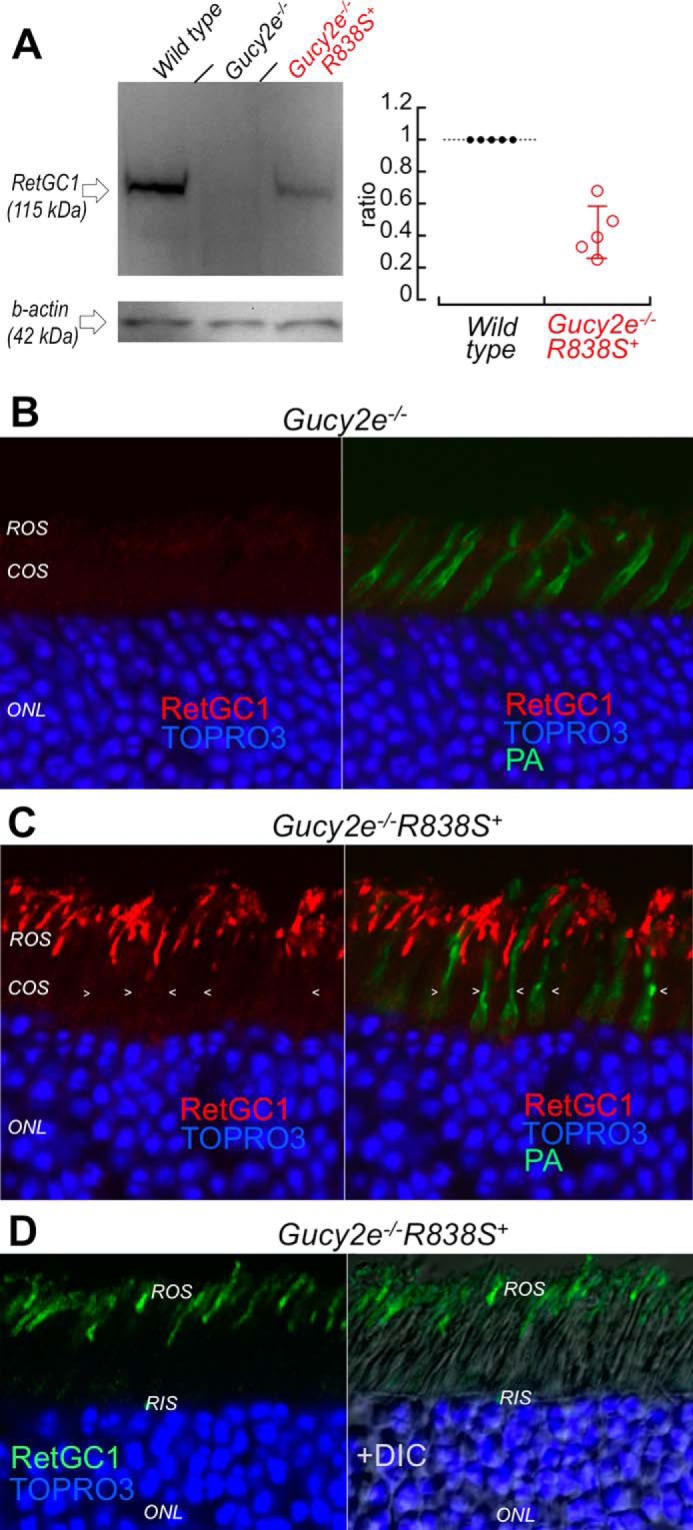
The R838S RetGC1 in the slower line 379 expressed at lower than the wild type mouse RetGC1 level localizes to rod outer segments. A, left: Western immunoblotting (left panel) of RetGC1 in 3-week-old wild type (left lane), Gucy2e−/− (middle) and the Gucy2e−/−R838S+ (right lane) mice. Right: integrated luminescence density of the R838S RetGC1 band in Gucy2e−/−R838S+ normalized by that of the endogenous mouse RetGC1 in wild type retinas on the same immunoblots semi-quantitatively estimates the transgene expression at 0.43 ± 0.16 mouse RetGC1 levels (error bar, standard deviation). B and C, R838S RetGC1 immunofluorescence in Gucy2e−/−R838S+ retinas. Paraformaldehyde-fixed retina sections from 3-week-old littermates were probed with anti-RetGC1 antibody (red) and peanut agglutinin (green fluorescence, superimposed in right panels), as described in the legend to Fig. 2D. Although RetGC1 is undetectable in Gucy2e−/− photoreceptors (panel B), the CORD6 RetGC1 appears in rods (ROS) but not in cones (COS, arrowheads) of their Gucy2e−/−R838S+ littermates (panel C). The samples in panels B and C were processed and stained in parallel and the images were recorded in the same experiment using identical settings for the anti-RetGC1 fluorescence imaging. D, the anti-RetGC1 fluorescence (green), superimposed on differential interference contrast (DIC, right panel), demonstrates that the R838S RetGC1 in the transgenic rods accumulates in the outer (ROS) rather than inner (RIS) segment.
