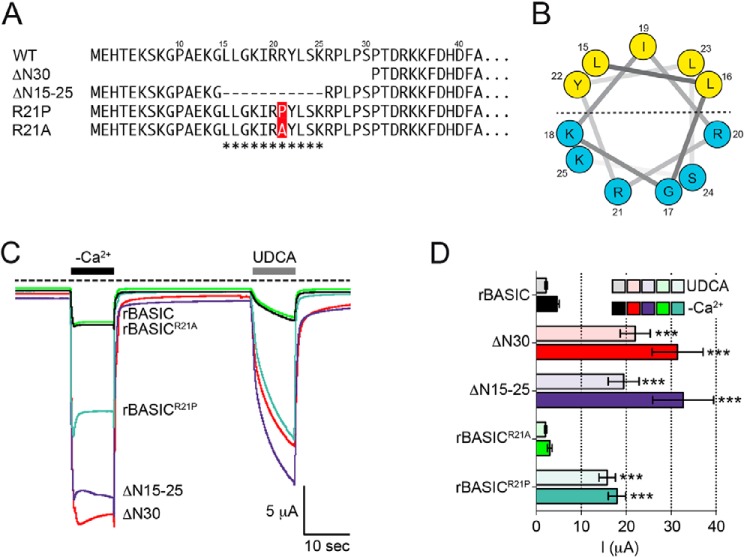
FIGURE 4.
Amphiphilic α-helix in the N-terminal region forms an inhibitory domain. A, representation of the N-terminal sequences of rBASIC, rBASIC ΔN30, rBASIC ΔN15–25, rBASICR21P, and rBASICR21A; the putative α-helix is labeled with asterisks. B, helical wheel representation of the putative amphiphilic α-helix. The numbers represent the amino acid positions of WT rBASIC. Color code of amino acid residues: yellow, hydrophobic; blue, hydrophilic. C, representative current traces showing the activation of WT rBASIC, rBASIC ΔN30, rBASIC ΔN15–25, rBASICR21P, and rBASICR21A by the removal of extracellular divalent cations (−Ca2+) or the application of 2 mm UDCA. D, quantitative comparison of current amplitudes induced by the removal of divalent cations (−Ca2+, solid bars) or by the application of 2 mm UDCA (transparent bars) as shown in C. Error bars, S.E., n = 9, ***, p < 0.001 (ANOVA).