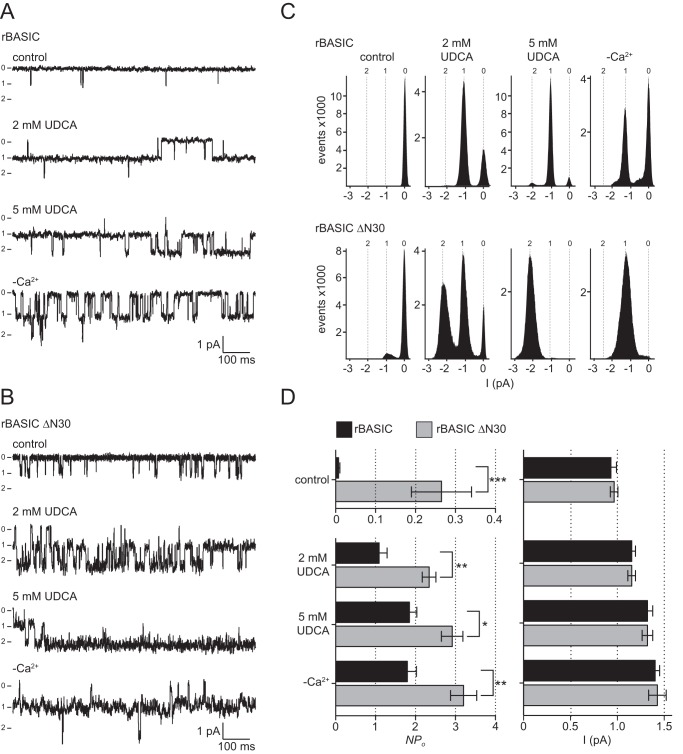
FIGURE 5.
Truncation of the N-terminal domain of rBASIC increases the open probability of the channel. A and B, representative segments of single channel current traces from outside-out patches from oocytes expressing rBASIC WT (A) or rBASIC ΔN30 (B). The traces were recorded at a holding potential of −60 mV in the absence of an activating stimulus (control), the presence of 2 mm UDCA or 5 mm UDCA, or in the absence of extracellular divalent cations (−Ca2+) (0 = closed state and 1, 2 = open states). Currents were recorded for 30 s after each solution exchange. C, single channel binned amplitude histograms; data points were obtained from 10-s segments, including the current traces shown in A and B. Histograms were used to determine the channel activity (NPo). D, left panel, summary of calculated NPo values for rBASIC WT and rBASIC ΔN30 under control condition and after activation with 2 or 5 mm UDCA or by removal of extracellular divalent cations (−Ca2+) obtained from eight recordings similar to the recordings shown in A. Right panel, summary of single channel current amplitudes of rBASIC WT and rBASIC ΔN30 under control conditions and after activation with 2 or 5 mm UDCA or by removal of extracellular divalent cations (−Ca2+) from similar recordings as shown in A or B. n = 8; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.001* (ANOVA).