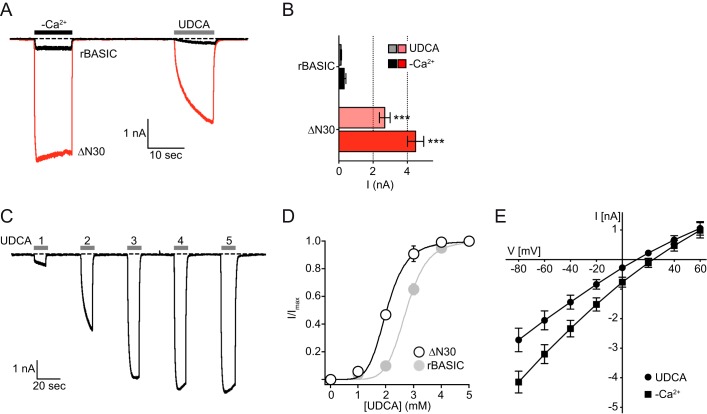
FIGURE 7.
Removal of the N-terminal domain of rBASIC increases its activity in HEK293 cells. A, representative current traces illustrating the activation of WT rBASIC and rBASIC ΔN30 expressed in HEK293 cells by the removal of extracellular divalent cations (−Ca2+) or by the application of 2 mm UDCA. B, quantitative comparison of current amplitudes induced by the removal of divalent cations (−Ca2+, solid bars) or by the application of 2 mm UDCA (transparent bars) as shown in A. Error bars, S.E., n = 8, ***, p < 0.001 (ANOVA). C, representative current trace illustrating the concentration-dependent activation of rBASIC ΔN30 by UDCA. D, concentration-response curve of rBASIC ΔN30 for UDCA. Currents were normalized to the maximum current in the presence of 5 mm UDCA, which was 5.72 ± 0.63 nA. Error bars, S.E., curves were fitted to the Hill equation (n = 8). For comparison, the concentration-response curve of WT rBASIC for UDCA is shown in light gray. E, mean current-voltage relationships of rBASIC ΔN30 in the absence of extracellular divalent cations (squares) and the presence of UDCA (circles). The holding potential was increased stepwise from −80 to +60 mV in 20-mV steps. Error bars, S.E.; n = 8.