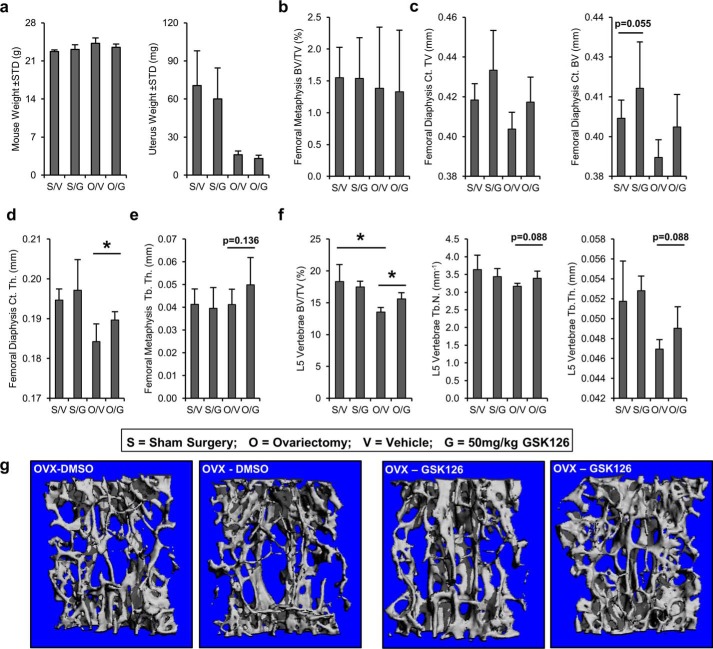
FIGURE 9.
Osteoprotective effects of Ezh2 inhibition skeletally mature mice. The effect of GSK126 was also analyzed using μCT analysis in a mouse ovariectomy model of hormone deficiency osteoporosis. Daily injections were performed for 6 weeks on each treatment group (n = 4–6/group). S, sham surgery; O, ovariectomy surgery; V, vehicle treatment (DMSO); G, 50 mg/kg GSK126 treatment. a, at sacrifice, body weights were similar between surgical and treatment groups, and uterus weights are reduced in the ovariectomized groups. b and c, analysis of bone volume in the femoral metaphysis (b) and femoral diaphysis (c). The data reveal a trend in cortical volume (Ct. TV) and cortical bone volume (Ct. BV) between vehicle- and GSK126-treated animals in both sham and OVX groups (compare S/V with S/G and O/V with O/G). d, assessment of femoral diaphysis shows increased cortical thickness (Ct. Th.) in OVX mice treated with GSK126 (compare O/V with O/G). e, analysis of femoral metaphysis trabecular thickness (Tb. Th.) shows a trend between vehicle- and GSK126-treated OVX animals (compare O/V with O/G). f, evaluation of L5 vertebrae. A reduction in bone volume fraction (BV/TV) in the spine is observed between sham and OVX animals (compare S/V with O/V), whereas GSK126 partially restores the loss of bone as a result of OVX surgery (compare O/V and O/G). g, examples of L5 spine μCT reconstructions OVX animals treated with vehicle (DMSO) or Ezh2 inhibitor (GSK126).