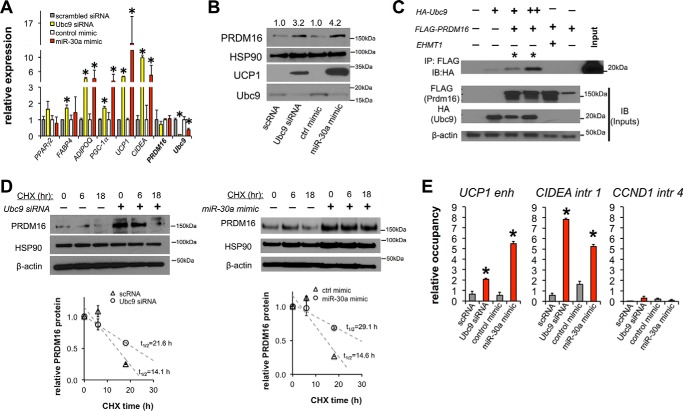
FIGURE 5.
PRDM16 stabilization and browning of human white adipocytes are regulated by the Ubc9/miR-30a axis. Ubc9 siRNA, miR-30a, or transfection controls were introduced into mature human adipocytes. A, the effects of Ubc9 siRNA and miR-30a overexpression in human adipocytes were characterized by qPCR analysis of PPARγ2, FABP4, ADIPOQ, PGC1α, UCP1, CIDEA, PRDM16, and Ubc9 mRNA levels (n ≥ 3 independent experiments; *, p < 0.05 relative to control transfections). B, expression levels of Ubc9, PRDM16, and UCP1 were analyzed by immunoblotting for human adipocytes transfected with Ubc9 siRNA or a miR-30a mimic. C, HEK293T cells were transfected with HA-Ubc9 and FLAG-PRDM16. Lysates were co-immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG antibodies, and the precipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting (IB). The interaction between EHMT1 and PRDM16 was a positive control for PRDM16 binding partners. D, PRDM16 protein levels in a cycloheximide (CHX) chase experiment were analyzed by immunoblotting (top panel) and quantified by densitometric analysis of PRDM16 protein degradation rates normalized to HSP90 expression (bottom panel, n = 2 independent experiments). E, PPARγ ChIP was performed in human adipocytes transfected with Ubc9 siRNA, miR-30a, or transfection controls. qPCR was used to analyze genomic occupancy using primers flanking PPARγ binding sites in the UCP1 enhancer (enh), and CIDEA intron (intr) 1 regions. An intronic region of Cyclin D1 served as a negative control (n = 2 independent experiments; *, p < 0.05 relative to control transfections). All data are expressed as mean ± S.E.