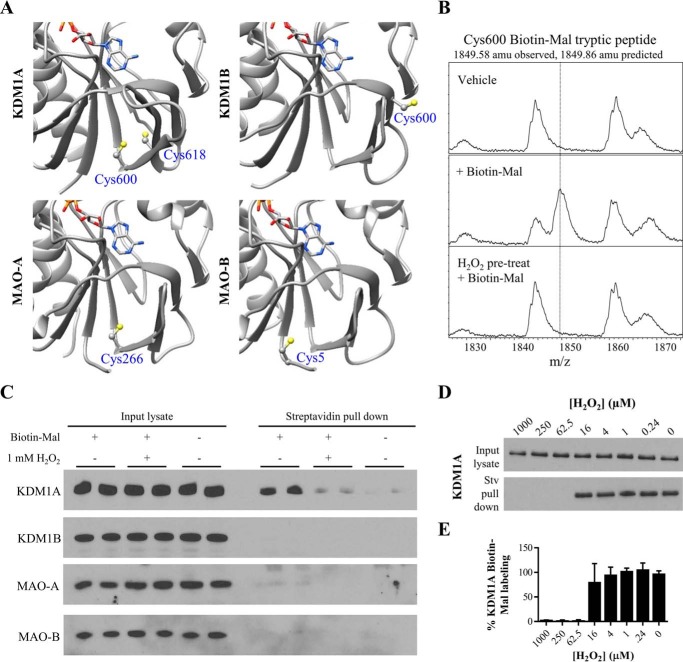
FIGURE 5.
KDM1A forms a putative intramolecular disulfide bond. A, crystal structures of the FAD-binding amine oxidase domains of KDM1A/B and MAO-A/B indicate a unique pair of proximal cysteine residues in KDM1A which may be capable of disulfide bond formation (respective PDB accession codes: 2HKO, 4GUU, 2BXR, and 2XFU, only residues in the amine oxidase domains are displayed). Cys-600 is ∼5 Å away from Cys-618 in the crystal structure of KDM1A, and this pair of cysteines abuts the Rossmann fold responsible for FAD cofactor binding. B, MALDI-TOF analysis of KDM1A tryptic digests reveals Biotin-Mal labeling of Cys-600 is blocked when KDM1A is pre-treated with H2O2. C, KDM1A is readily labeled with 10 μm Biotin-Mal in SH-SY5Y cell lysate and pulled down on streptavidin-agarose beads, and labeling is blocked by pulse pre-treatment (10 min) of intact cells with 1 mm H2O2. Other FAD-dependent amine oxidases do not appear to be as thiol-reactive. D, dose response curve of pulse pre-treatment (10 min) of intact SH-SY5Y cells with H2O2. E, quantification of KDM1A Biotin-Mal labeling, n = 2 assays from biological duplicates. Error bars indicate S.D.