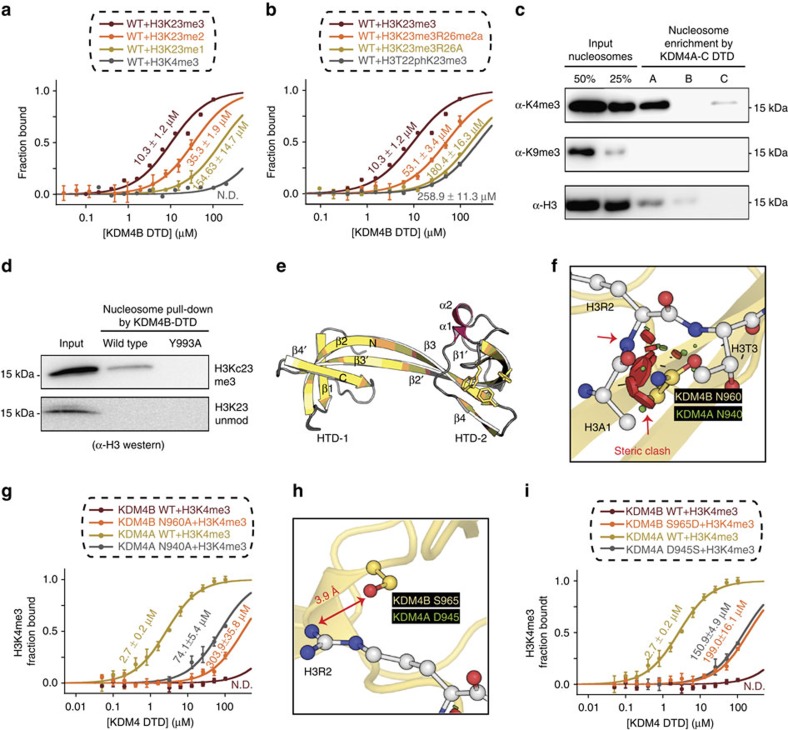
Figure 4. KDM4B-DTD is an H3K23me3-specific reader.
(a,b) Conserved interaction between KDM4B-DTD and H3K23me3 as determined by FP. (c) MARCC confirms enrichment of H3K4me3-containing chromatin by KDM4A and KDM4C but not KDM4B. HaloTag-tagged DTDs are immobilized on resin and incubated with native mononucleosomes purified from MCF-7 cells. Enriched nucleosomes are eluted with SDS sample buffer and probed by indicated antibodies. (d) Recombinant KDM4B-DTD wild type pulls down H3Kc23me3-containing MLA nucleosome (H3Kc23me3Kc36me3). Aromatic cage mutant KDM4B-DTD Y993A and H3K23 unmodified-containing MLA nucleosome (H3K23unmodKc36me3) were included as controls. (e) Based on the structural alignment of HTD-2 domains, H3(19–27)K23me3 peptide from KDM4A structures is modelled into KDM4B-DTD apo structure (PDB ID: 4UC4). See Methods for details. (f–i) Key residues contributing to decreased H3K4me3 binding identified from KDM4B-H3K4me3 model. Steric clash (red disk: major clash) between KDM4B N960 and H3A1/R2 (f,g). Decreased interaction between KDM4B S965 and H3R2 (h,i). Corresponding residues in KDM4A are labelled. Enhanced H3K4me3 binding by KDM4B mutants N960A and S965D. As controls, corresponding mutants in KDM4A are examined for H3K4me3 binding. (a,b,g,i) Binding affinity of corresponding protein-peptide combinations is quantified by FP. Errors represent s.d. from three experimental replicates.