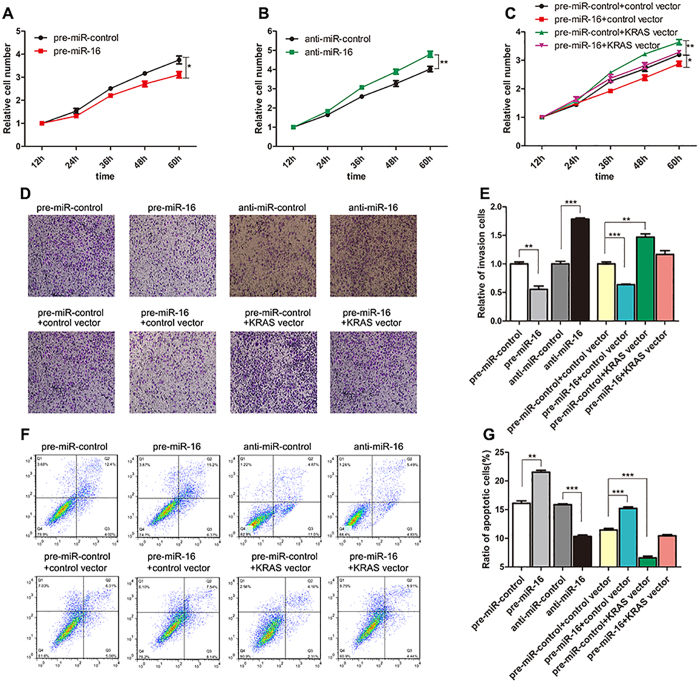
Figure 4. Effect of miR-16 and KRAS on the proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of CRC cells.
(A) Cell proliferation assays were performed 12, 24, 36, 48 and 60 h after the transfection of SW480 cells with pre-miR-16 or pre-miR-control. (B) Cell proliferation assays were performed 12, 24, 36, 48 and 60 h after the transfection of Caco2 cells with anti-miR-16 or anti-miR-control. (C) Cell proliferation assays were performed 12, 24, 36, 48 and 60 h after the transfection of SW480 cells with pre-miR-control plus a control plasmid, pre-miR-control plus a KRAS overexpression plasmid, pre-miR-16 plus a control plasmid, or pre-miR-16 plus a KRAS overexpression plasmid. (D and E) Transwell analysis of SW480 cells transfected with pre-miR-16 or pre-miR-control, or with pre-miR-control plus a control plasmid, pre-miR-control plus a KRAS overexpression plasmid, pre-miR-16 plus a control plasmid, or pre-miR-16 plus a KRAS overexpression plasmid. At the same time, Caco2 cells were transfected with anti-miR-16 or anti-miR-control and then subjected to Transwell analysis. D: representative image; E: quantitative analysis. (F and G) An apoptosis assay was performed 48 h after the transfection of SW480 cells with pre-miR-16 or pre-miR-control, or with pre-miR-control plus a control plasmid, pre-miR-control plus a KRAS overexpression plasmid, pre-miR-16 plus a control plasmid, or pre-miR-16 plus a KRAS overexpression plasmid. At the same time, Caco2 cells were transfected with anti-miR-16 or anti-miR-control and then subjected to apoptosis analysis. Cell apoptosis profiles were analyzed by flow cytometry. F: representative image; G: quantitative analysis. (mean ± S.D.; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).