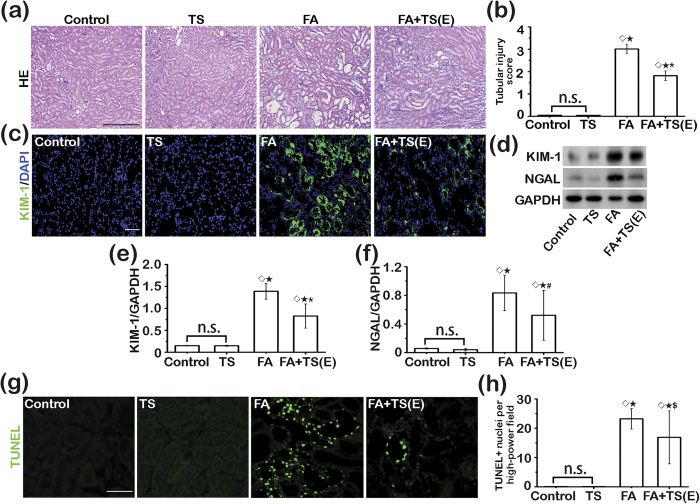
Figure 4. Early Tanshinone IIA treatment protects against folic acid-induced renal tubular damage.
(a) Representative micrographs showing hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining of kidney specimens procured on day 3. Scale bar = 500 μm. (b) Kidney tubular injury score assessed based on evaluation of HE staining. ◊P < 0.001 vs Control; ★P < 0.001 vs TS; *P < 0.001 vs FA; n.s., not significant. (c) Representative micrographs showing immunofluorescent staining of kidney specimens procured on day 3 for kidney injury molecule-1(KIM-1). Sections were counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Scale bar = 200 μm. (d) Representative immunoblots of KIM-1 and neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) in cortical kidney lysates. (e) and (f) Relative abundance of KIM-1 (e) and NGAL (f) in immunoblots expressed as densitometric ratios of KIM-1/GAPDH or NGAL/GAPDH; ◊P < 0.001 vs Control; ★P < 0.001 vs TS; *P < 0.001 vs FA; #P = 0.004 vs FA; n.s., not significant; (n = 9). (g) Representative micrographs showing TUNEL staining of kidney specimens procured on day 3. Scale bar = 200 μm. (h) Absolute counting of TUNEL-positive nuclei per high power field. ◊P < 0.001 vs Control; ★P < 0.001 vs TS; $P = 0.009 vs FA; n.s., not significant; (n = 9).