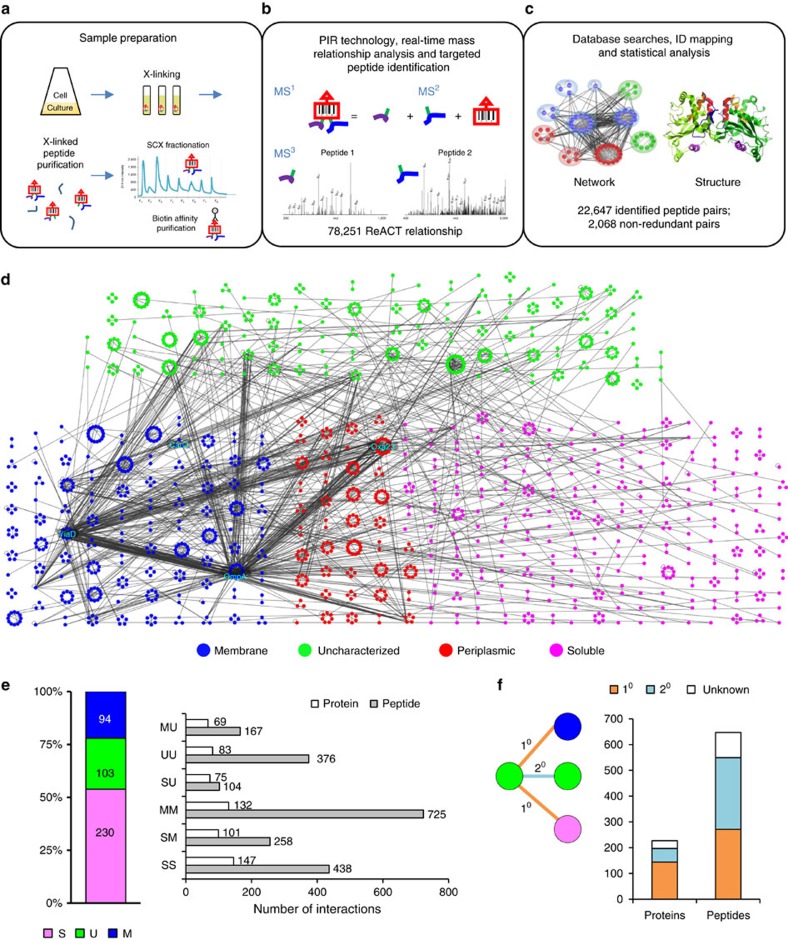
Figure 1. Identification of in vivo protein interactions in A. baumannii cells.
(a–c) Schematic overview of experimental procedures. (d) Protein interaction network in AB5075 cells comprising 2,068 non-redundant cross-linked peptide pairs. Nodes indicate the identified cross-linked sites and were grouped into circles to represent proteins. Node colours illustrate the protein primary subcellular localization. Blue, membrane proteins; green, uncharacterized proteins; magenta, soluble proteins; red, soluble proteins predicted to be localized in periplasm47,48. Edges represent the identified cross-links between the two sites. Protein interaction hubs OmpA, YiaD and Oxa-23, as well as OM porin CarO are highlighted. Uncharacterized proteins were identified cross-linked to membrane, periplasmic and soluble proteins. (e) Composition of protein nodes (M, membrane proteins; S, soluble proteins; U, uncharacterized proteins) and edges in the network based on subcellular localization. Edges: MM, cross-links between membrane proteins; MU, cross-links of membrane proteins to uncharacterized proteins; SM, cross-links of membrane proteins to soluble proteins; SS, cross-links between soluble proteins; SU, cross-links of soluble proteins to uncharacterized proteins; UU, cross-links between uncharacterized proteins. (f) Cross-links between the uncharacterized proteins and the functionally annotated proteins, either directly (1° interactions) or through an intermediate partner (2° interactions), could shed light on the function for these uncharacterized proteins.