Fig. 1.
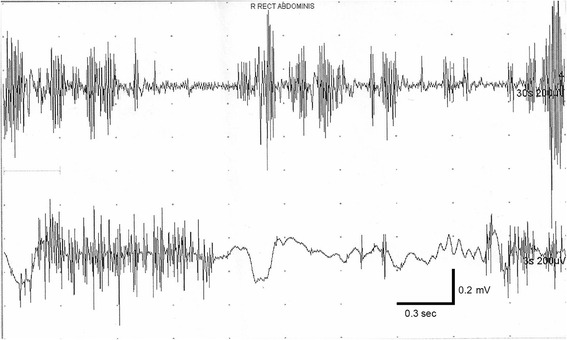
Needle electromyographic (EMG) recordings of the abdominal muscles showed abnormal motor unit potential discharges, some of them tonic, varying over a wide range of frequency from 3–5 to 30–40 sec. In addition, sudden discharges from groups of motor unit potentials was seen lasting from as brief as 10–20 msec to over 3–5 sec. The discharges were arrhythmical and asynchronous in separate muscles. They were also repetitive but highly unpredictable
