Fig. 5.
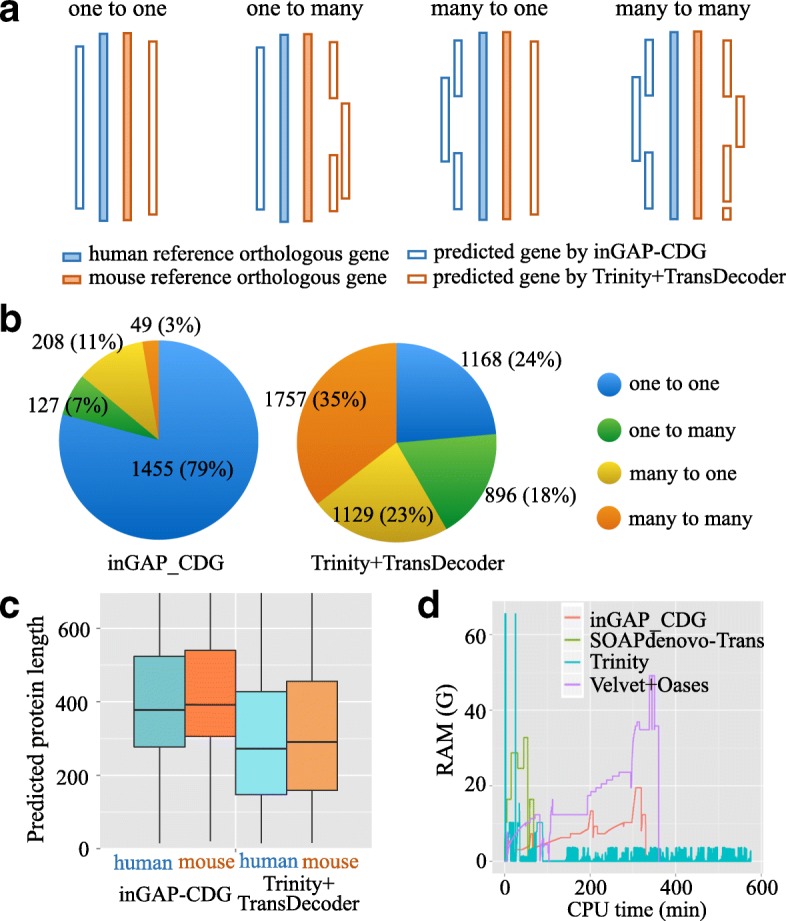
Application of inGAP-CDG on orthologous gene construction and its computational efficiency. RNA-seq datasets from human and mouse brain tissues were used to evaluate the performance of inGAP-CDG and Trinity + TransDecoder on detecting orthologous gene pairs. a Based on the alignments of predicted genes to reference orthologous gene groups, predicted orthologs can be classified into four groups. Only the ‘one-to-one’ group can be recognized as authentic orthologous pairs by classical orthology inference methods. b inGAP-CDG predicted more ‘one-to-one’ type orthologs than Trinity + TransDecoder. c The length distribution of predicted genes by the two methods. d Comparison of the running time and RAM usage among the four methods (inGAP-CDG, Trinity, Soapdenovo-Trans, Velvet + Oases) using the publicly available RNA-seq dataset (SRR1045067)
