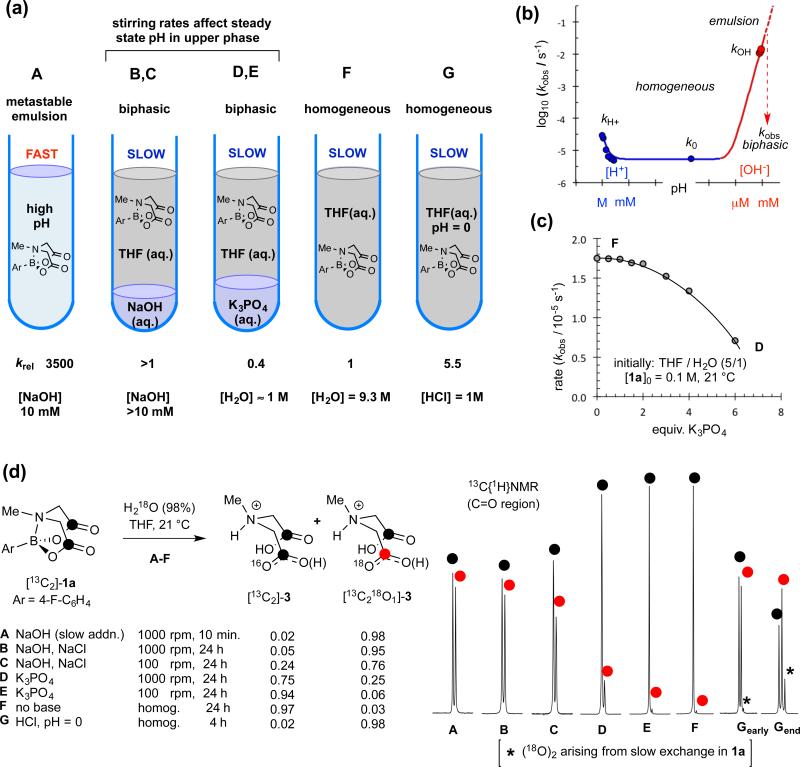
Figure 2. Distinction of limiting pathways for basic (fast, A), neutral (slow, F) and acidic (G) hydrolysis of 1a.
(a) Schematic representation of conditions A-G; (b) pH rate profile; arbitrary pH scale (autoprotolysis constant of 0.5 mol-fraction aq. THF estimated as pKapp = 20).12 Hydrolysis of water-soluble Me-B(MIDA) in aqueous buffer (pH 1-11) confirms kobs = kH+[H+] + k0 + kOH[OH−]. (c) Impact of K3PO4 on hydrolysis rate under heterogeneous conditions. Line through data is an aid to the eye. (d) 13C{1H}NMR Sub-spectra (178.70-178.85 ppm; ΔδC18O/16O = 30 ppb) of MIDA ligand (3) from hydrolysis of [13C2]-1a in THF/18OH2 under conditions A to G; see Supplementary Figures 4 and 5 confirming slow 18O exchange in 1a but not in 3 under acidic conditions (Gearly:25% conversion, Gend:>98 % conversion) and no exchange in 1a, and very slow 18O exchange in 3 (≤1.4%, 48 h) under neutral conditions.