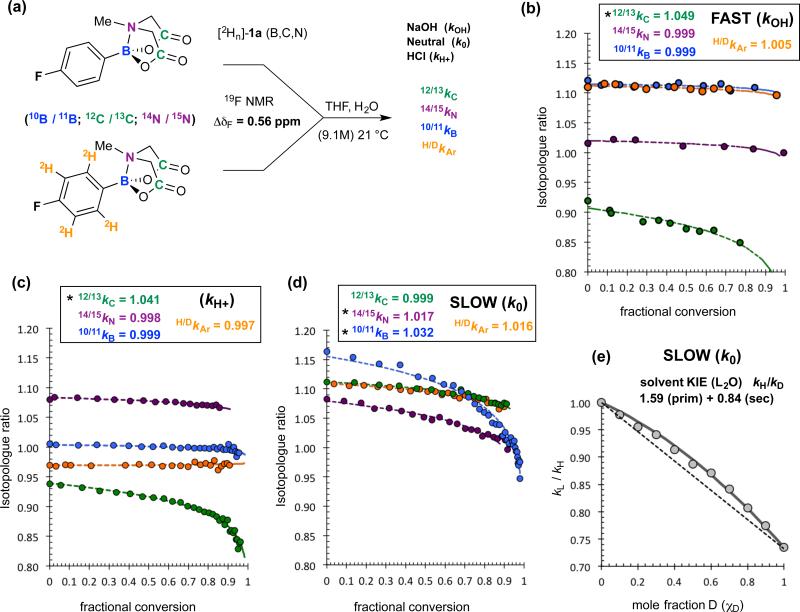
Figure 4. Kinetic isotope effects (KIEs) for Ar-B(MIDA) (1a) hydrolysis.
(a) outline of methodology allowing KIE values to be extracted by a standard pseudo first-order competition model; heavy atom KIEs shown are those after correction for aryl deuteration,17,18 net-σD = −6.3(±0.15) × 10−3, and competing processes (kH+ + k0). (b) Fast hydrolysis: substoichiometric aq. NaOH added to vigorously stirred solutions of 1a (10 mM) to attain a suitable span of fractional conversions. Hydrolysis post phase-separation inhibited by addition of anhydrous MgSO4. (c) Acidic hydrolysis (1M HCl) analysed in situ. (d) Neutral hydrolysis analysed in situ. Identical KIES (Δ≤ ±0.002) were obtained with 0.5 M H2O. (e) Proton inventory conducted with 1a in THF/L2O (9.1 M, L = H, D). The net solvent KIE (χD = 1) increases from 1.4 to 2.0 as [D2O] is decreased from 9.1 to 0.5 M.